Rev. 5.00, 09/03, page 21 of 760
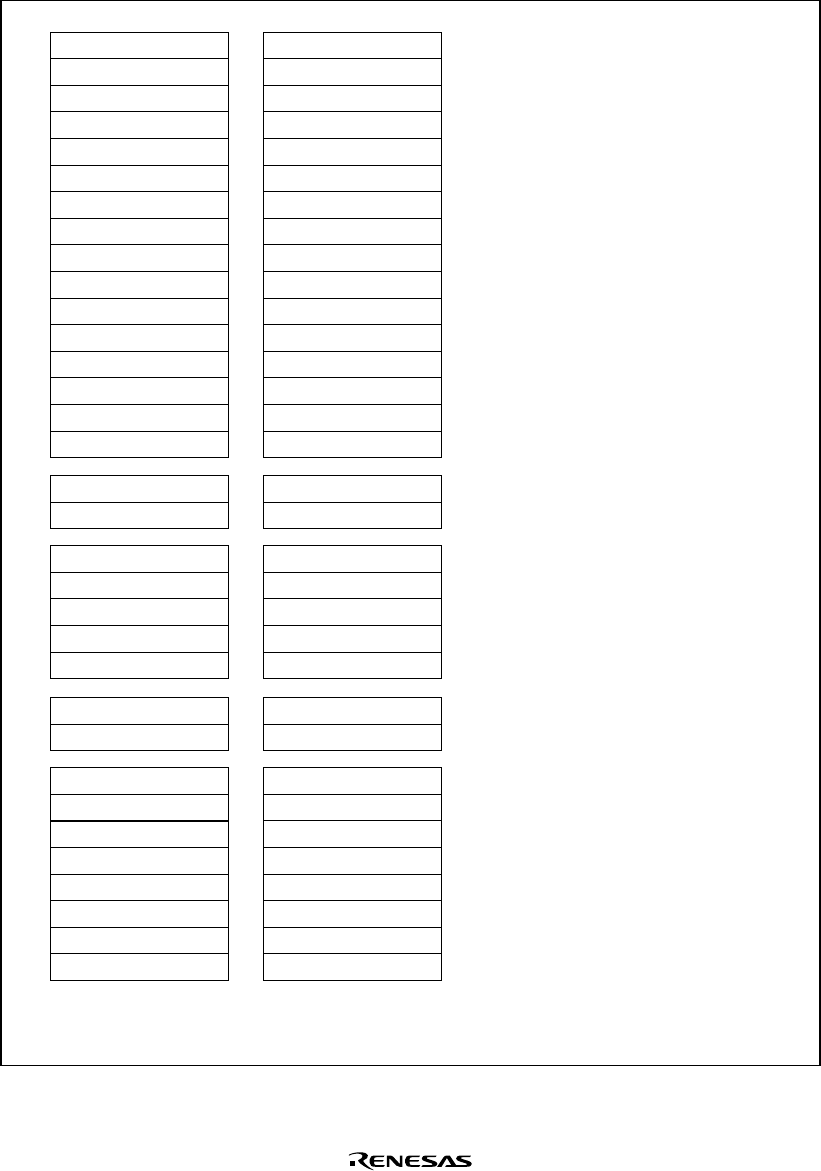
R0_BANK1
*1 *2
R1_BANK1
*2
R2_BANK1
*2
R3_BANK1
*2
R4_BANK1
*2
R5_BANK1
*2
R6_BANK1
*2
R7_BANK1
*2
R8
R9
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
SR
SSR
PC
SPC
GBR
MACH
MACL
PR
VBR
31 0
a. Privileged mode
register configuration
(RB = 1)
R0_BANK0
*1 *3
R1_BANK0
*3
R2_BANK0
*3
R3_BANK0
*3
R4_BANK0
*3
R5_BANK0
*3
R6_BANK0
*3
R7_BANK0
*3
R0_BANK0
*1 *3
R1_BANK0
*3
R2_BANK0
*3
R3_BANK0
*3
R4_BANK0
*3
R5_BANK0
*3
R6_BANK0
*3
R7_BANK0
*3
R8
R9
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
SR
SSR
PC
SPC
GBR
MACH
MACL
PR
VBR
31 0
b. Privileged mode
register configuration
(RB = 0)
R0_BANK1
*1 *2
R1_BANK1
*2
R2_BANK1
*2
R3_BANK1
*2
R4_BANK1
*2
R5_BANK1
*2
R6_BANK1
*2
R7_BANK1
*2
Notes:
1.
2.
3.
R0 functions as an index
register in the indexed
register-indirect addressing
mode and indexed GBR-
indirect addressing mode.
Banked register
When the RB bit of the SR
register is 1, the register can
be accessed for general use.
When the RB bit is 0, it can
only be accessed with the
LDC/STC instruction.
Banked register
When the RB bit of the SR
register is 0, the register can
be accessed for general use.
When the RB bit is 1, it can
only be accessed with the
LDC/STC instruction.
Figure 2.2 Privileged Mode Register Configuration


















