Rev. 5.00, 09/03, page 354 of 760
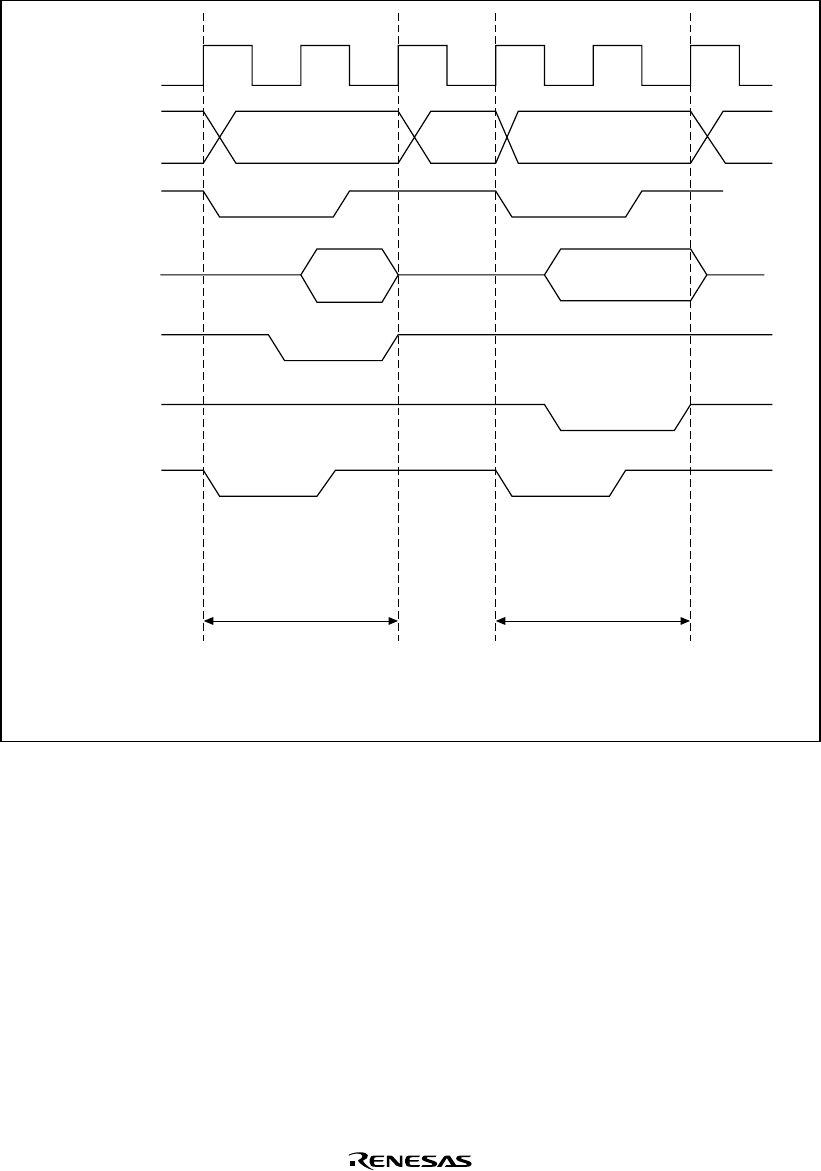
(1st cycle) (2nd cycle)
Data read cycle Data write cycle
Transfer source
address
Transfer destination
address
CKIO
A25 to A0
CSn
D31 to D0
RD
WEn
DACKn
Note: In transfer between external memories, with DACK output in the read cycle, DACK
output timing is the same as that of CSn.
Figure 11.6 Example of DMA Transfer Timing in the Direct Address Mode in Dual Mode
(Transfer Source: Ordinary Memory, Transfer Destination: Ordinary Memory)
(2) In indirect address transfer mode, the address of memory in which data to be transferred is
stored is specified in the transfer source address register (SAR3) in the DMAC.
Consequently, in this mode, the address value specified in the transfer source address
register in the DMAC is read first. This value is temporarily stored in the DMAC. Next,
the read value is output as an address, and the value stored in that address is stored in the
DMAC again. Then, the value read afterwards is written to the address specified in the
transfer destination address; this completes one DMA transfer. 16-byte transfer is not
possible.
Figure 11.7 shows an example. In this example, the transfer destination, the transfer
source, and the storage destination of the indirect address are 16-bit external memories,
and transfer data is 16 or 8 bits. Figure 11.8 shows an example of the transfer timing.


















