Rev. 5.00, 09/03, page 474 of 760
14.3.4 Synchronous Operation
In synchronous mode, the SCI transmits and receives data in synchronization with clock pulses.
This mode is suitable for high-speed serial communication.
The SCI transmitter and receiver are independent, so full-duplex communication is possible while
sharing the same clock. The transmitter and receiver are also double buffered, so continuous
transmitting or receiving is possible by reading or writing data while transmitting or receiving is in
progress.
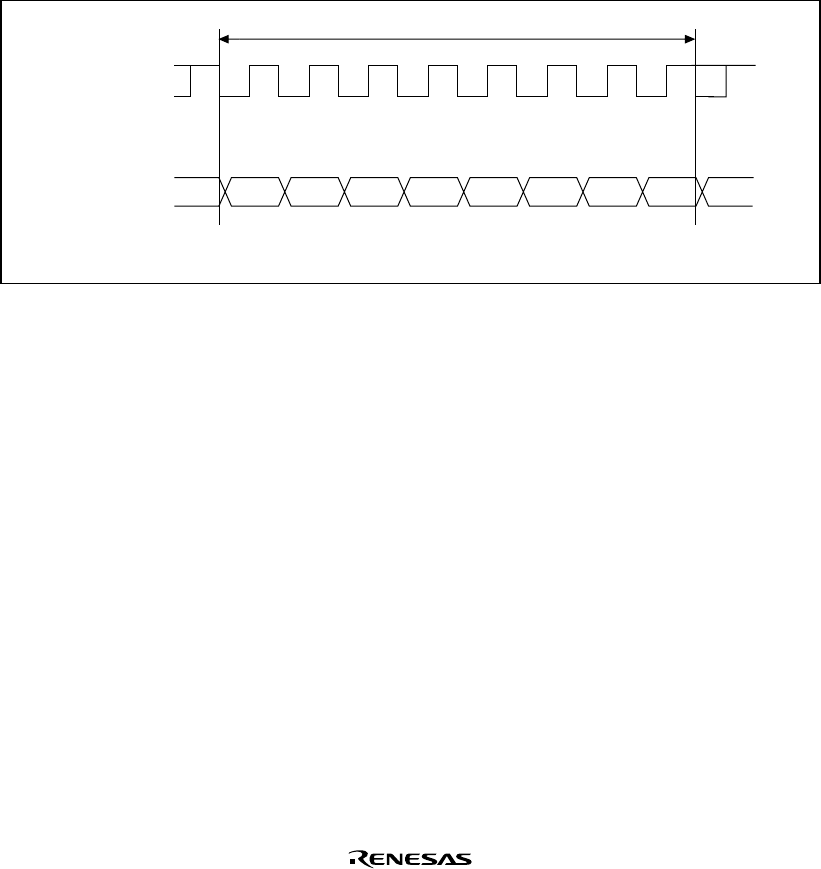
Figure 14.17 shows the general format in synchronous serial communication.
Bit 0Don't care Don't careBit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7
LSB MSB
Serial clock
Serial data
**
One unit of communication data (character or frame)
Note: * High except in continuous transmitting or receiving
Figure 14.17 Data Format in Synchronous Communication
In synchronous serial communication, each data bit is output on the communication line from one
falling edge of the serial clock to the next. Data is guaranteed valid at the rising edge of the serial
clock. In each character, the serial data bits are transmitted in order from the LSB (first) to the
MSB (last). After output of the MSB, the communication line remains in the state of the MSB. In
synchronous mode, the SCI transmits or receives data by synchronizing with the falling edge of
the serial clock.
Communication Format: The data length is fixed at eight bits. No parity bit or multiprocessor bit
can be added.