Rev. 5.00, 09/03, page 203 of 760
Section 9 On-Chip Oscillation Circuits
9.1 Overview
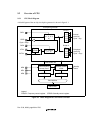
The on-chip oscillation circuits consist of a clock pulse generator (CPG) block and a watchdog
timer (WDT) block. The WDT is a single-channel timer that counts the clock settling time and is
used when clearing standby mode and temporary standbys, such as frequency changes. It can also
be used as an ordinary watchdog timer or interval timer.
9.1.1 Features
The CPG has the following features:
• Four clock modes: Selection of four clock modes for different frequency ranges, power
consumption, direct crystal input, and external clock input.
• Three clocks generated independently: An internal clock for the CPU, cache, and TLB (Iφ); a
peripheral clock (Pφ) for the on-chip peripheral modules; and a bus clock (CKIO) for the
external bus interface.
• Frequency change function: Internal and peripheral clock frequencies can be changed
independently using the PLL circuit and divider circuit within the CPG. Frequencies are
changed by software using frequency control register (FRQCR) settings.
• Power-down mode control: The clock can be stopped for sleep mode and standby mode and
specific modules can be stopped using the module standby function.
The WDT has the following features:
• Can be used to ensure the clock settling time: Use the WDT to cancel standby mode and the
temporary standbys which occur when the clock frequency is changed.
• Can switch between watchdog timer mode and interval timer mode.
• Generates internal resets in watchdog timer mode: Internal resets occur after counter overflow.
Selection of power-on reset or manual reset.
• Generates interrupts in interval timer mode: Internal timer interrupts occur after counter
overflow.
• Selection of eight counter input clocks. Eight clocks (×1 to ×1/4096) can be obtained by
dividing the peripheral clock.