Rev. 5.00, 09/03, page 207 of 760
9.3 Clock Operating Modes
Table 9.3 shows the relationship between the mode control pin (MD2–MD0) combinations and the
clock operating modes. Table 9.4 shows the usable frequency ranges in the clock operating modes.
Table 9.3 Clock Operating Modes
Pin Values Clock I/O
Mode MD2 MD1 MD0 Source Output
PLL2
On/Off
PLL1
On/Off
Divider 1
Input
Divider 2
Input
CKIO
Frequency
0 0 0 0 EXTAL CKIO On,
multi-
plication
ratio: 1
On PLL1
output
PLL1 (EXTAL)
1 0 0 1 EXTAL CKIO On,
multi-
plication
ratio: 4
On PLL1
output
PLL1 (EXTAL) × 4
2 010 Crystal
oscillator
CKIO On,
multi-
plication
ratio: 4
On PLL1
output
PLL1 (Crystal) × 4
7 1 1 1 CKIO — Off On PLL1
output
PLL1 (CKIO)
— Except above
value
Reserved
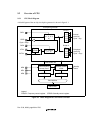
Mode 0: An external clock is input from the EXTAL pin and undergoes waveform shaping by
PLL circuit 2 before being supplied inside the chip. PLL circuit 1 is constantly on. An input clock
frequency of 25 MHz to 66.67 MHz can be used, and the CKIO frequency range is 25 MHz to
66.67 MHz.
Mode 1: An external clock is input from the EXTAL pin and its frequency is multiplied by 4 by
PLL circuit 2 before being supplied inside the chip, allowing a low-frequency external clock to be
used. An input clock frequency of 6.25 MHz to 16.67 MHz can be used, and the CKIO frequency
range is 25 MHz to 66.67 MHz.
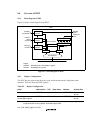
Mode 2: The on-chip crystal oscillator operates, with the oscillation frequency being multiplied
by 4 by PLL circuit 2 before being supplied inside the chip, allowing a low crystal frequency to be
used. A crystal oscillation frequency of 6.25 MHz to 16.67 MHz can be used, and the CKIO
frequency range is 25 MHz to 66.67 MHz.