Rev. 5.00, 09/03, page 59 of 760
H'80000000
H'A0000000
H'C0000000
H'E0000000
H'FFFFFFFF
2-Gbyte virtual space,
cacheable
(write-back/write-through)
2-Gbyte virtual space,
cacheable
(write-back/write-through)
Address error
H'00000000H'00000000
H'80000000
H'FFFFFFFF
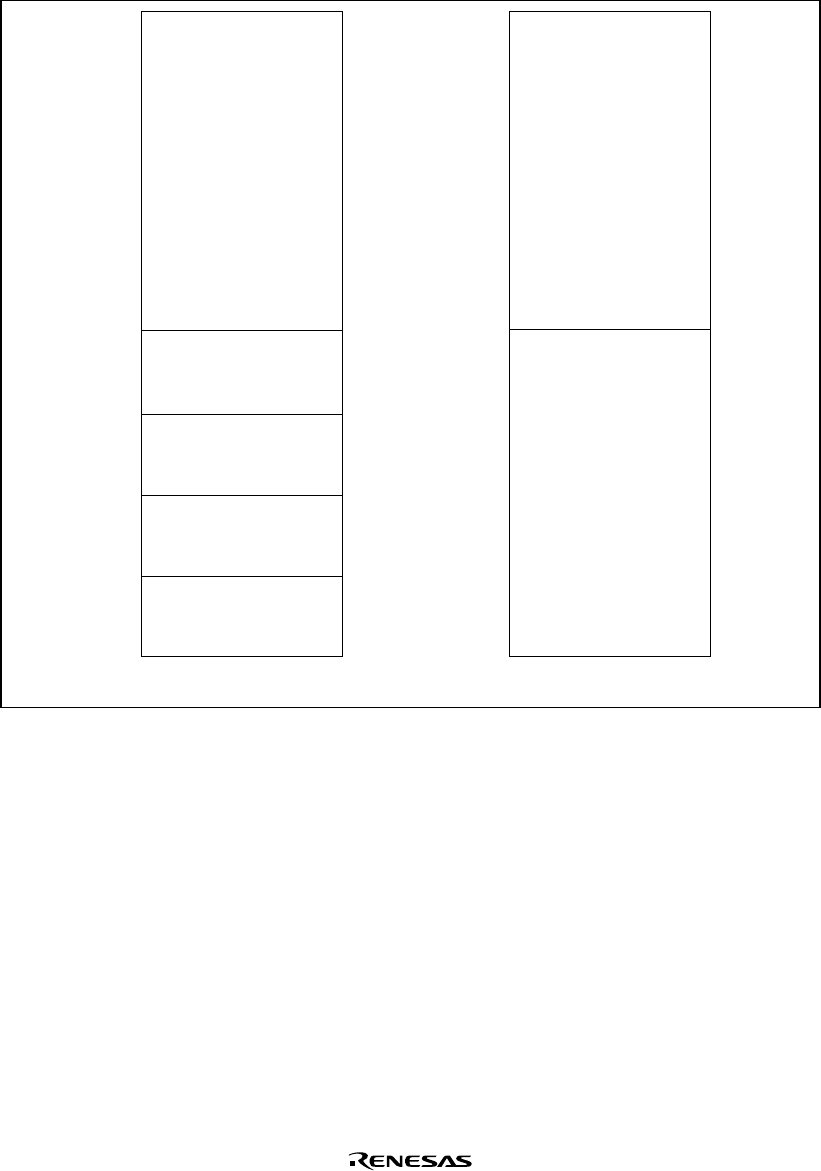
Area P0
Area P1
Area P2
Area P3
Area P4
Area U0
Privileged mode User mode
0.5-Gbyte fixed physical
space, cacheable
(write-back/write-through)
0.5-Gbyte fixed
physical space,
non-cacheable
0.5-Gbyte virtual space,
cacheable
(write-back/write-through)
0.5-Gbyte control space,
non-cacheable
Figure 3.2 Virtual Address Space Mapping
Physical Address Space: The SH7709S supports a 32-bit physical address space, but the upper 3
bits are actually ignored and treated as a shadow. See section 10, Bus State Controller (BSC), for
details.
Address Translation: When the MMU is enabled, the virtual address space is divided into units
called pages. Physical addresses are translated in page units. Address translation tables in external
memory hold information such as the physical address that corresponds to the virtual address and
memory protection codes. When an access to an area other than P4 occurs, if the accessed virtual
address belongs to area P1 or P2 there is no TLB access and the physical address is uniquely
defined. If it belongs to area P0, P3, or U0, the TLB is searched by virtual address and, if that
virtual address is registered in the TLB, the access hits the TLB. The corresponding physical
address and the page control information are read from the TLB and the physical address is
determined.


















