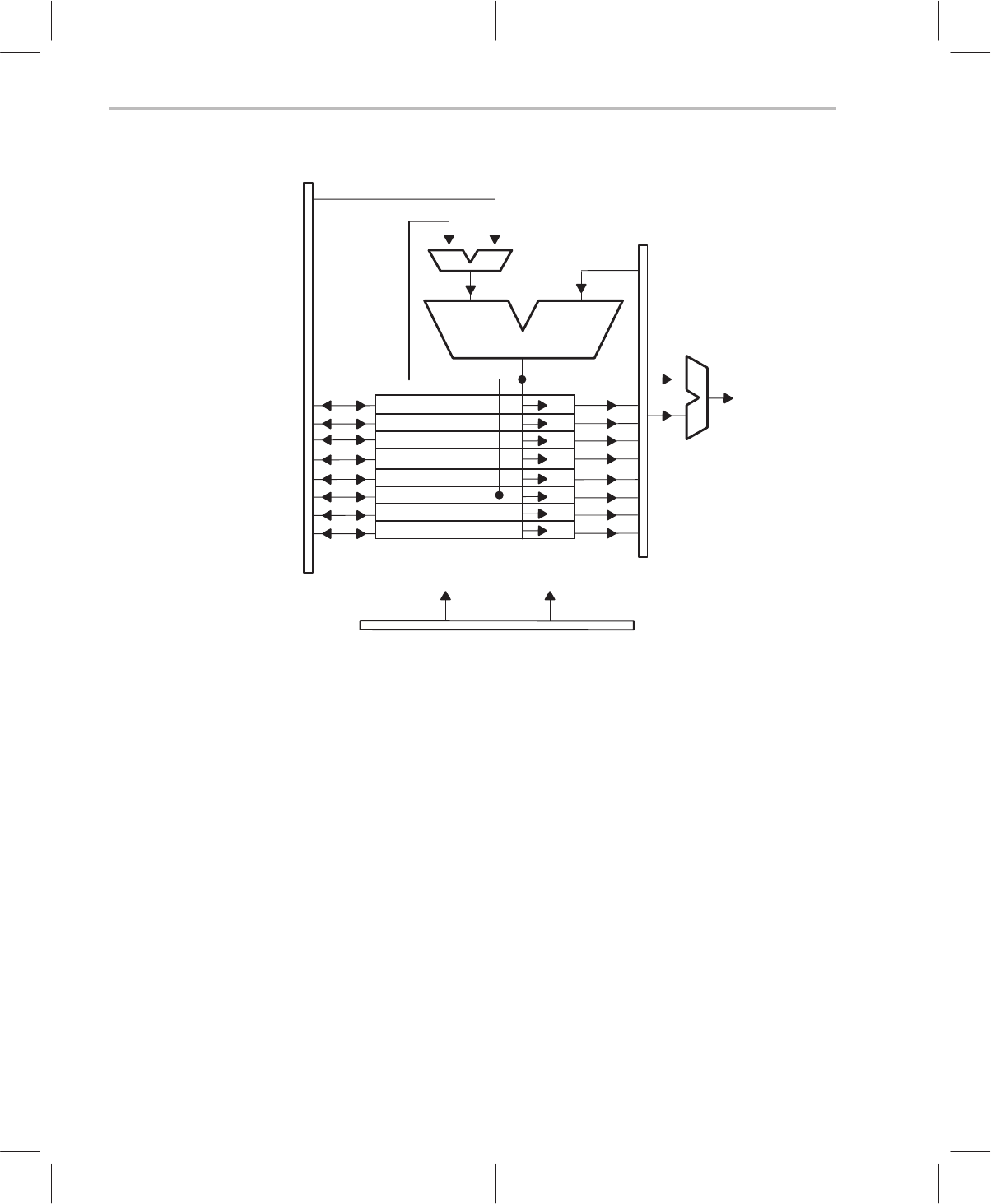
Data Memory Address Unit
2-12
Figure 2–6. Data Memory Address Unit
R3
R2
R1
R0
R7
R6
R5
R4
Internal
Databus
Arithmetic Block
RAM Address
Internal Program Bus
Register Addressing Mode
STACK
PAGE
INDEX
LOOP
2.3.1 RAM Configuration
The data memory block (RAM) is physically organized into 17-bit parallel
words. Within each word, the extra bit (bit 16) is used as a flag bit or tag for
op-codes in the instruction set. Specifically, the flag bit directs complex branch
conditions associated with certain instructions. The flag bit is also used by the
computational unit for signed or unsigned arithmetic operations (see
Section 2.2.1,
Multiplier
).
The size of the C614 RAM block is 640 17-bit locations. Each address provided
by the DMAU causes 17 bits of data to be addressed. These 17 bits are
operated on in different ways, depending on the instructions being executed.
For most instructions, the data is interpreted as 16-bit word format. This means
that bits 0 through 15 are used, and bit 16 is either ignored or designated as
a flag or status bit.