Instruction Syntax and Addressing Modes
4-12
For any particular addressing mode, replace the {
adrs
} with the syntax shown
in Table 4–4. To encode the instruction, replace the
am
, R
x
and
pm
bits with
the bits required by the addressing mode (Table 4–4). For example, the
instruction MOV A
n
[~], {
adrs
} [,
next A
] indicates all of the following (only partial
combinations are shown):
MOV A0, *0xab12 ;
n
= 0, {
adrs
} =
dma16
= 0xab12
MOV A1, *R6+0x2f, ++A ;
n
= 1, {
adrs
} = *R6+0x2f,
offset7
= 0x2f,
[
next A
] = ++A
MOV A2~, *R0+R5, ––A ;
n
= 2, {
adrs
} = *R0+R5,
x
= 0, [
next A
] = ––A
MOV A3, *R1+0x12ef ;
n
= 3, {
adrs
} = *R1+0x12ef,
x
= 1,
offset16
= 0x12ef
MOV A0, *R2 ;
n
= 0, {
adrs
} = *R2,
x
= 2
MOV A1, *R3++, ––A ;
n
= 1, {
adrs
} = *R3++,
x
= 3, [
next A
] = ––A
MOV A2~, *R4–– ;
n
= 2, {
adrs
} = *R4––,
x
= 4
MOV A3, *R7++R5, ++A ;
n
= 3, {
adrs
} = *R7++R5,
x
= 7, [
next A
] = ++A
Flag instructions apply to certain classes of instructions (Class 8a). They ad-
dress only the flag bit by either a 6 bit global address or a 6 bit relative address
from the indirect register R6. If bit 0 of these instructions is 0, then bits 1 to 6
of the opcode are taken as the bit address starting from data memory location
0000h. If bit 0 is 1, then bits 1 to 6 are used as an offset from the page register
R6 to compute the relative address. Bits 0 to 6 of flag instructions are written
as {
flagadrs
} throughout this manual. When this symbol appears, it should be
replaced by the syntax and bits shown in Table 4–7
For example, AND TF
n
, {
flagadrs
} can be written as follows (not all possible
combinations are shown):
AND TF1, *0x21 ; global flag addressing, flag address is 0x21 absolute
AND TF2, *R6+0x21 ; relative flag addressing, flag address is R6+0x21
absolute
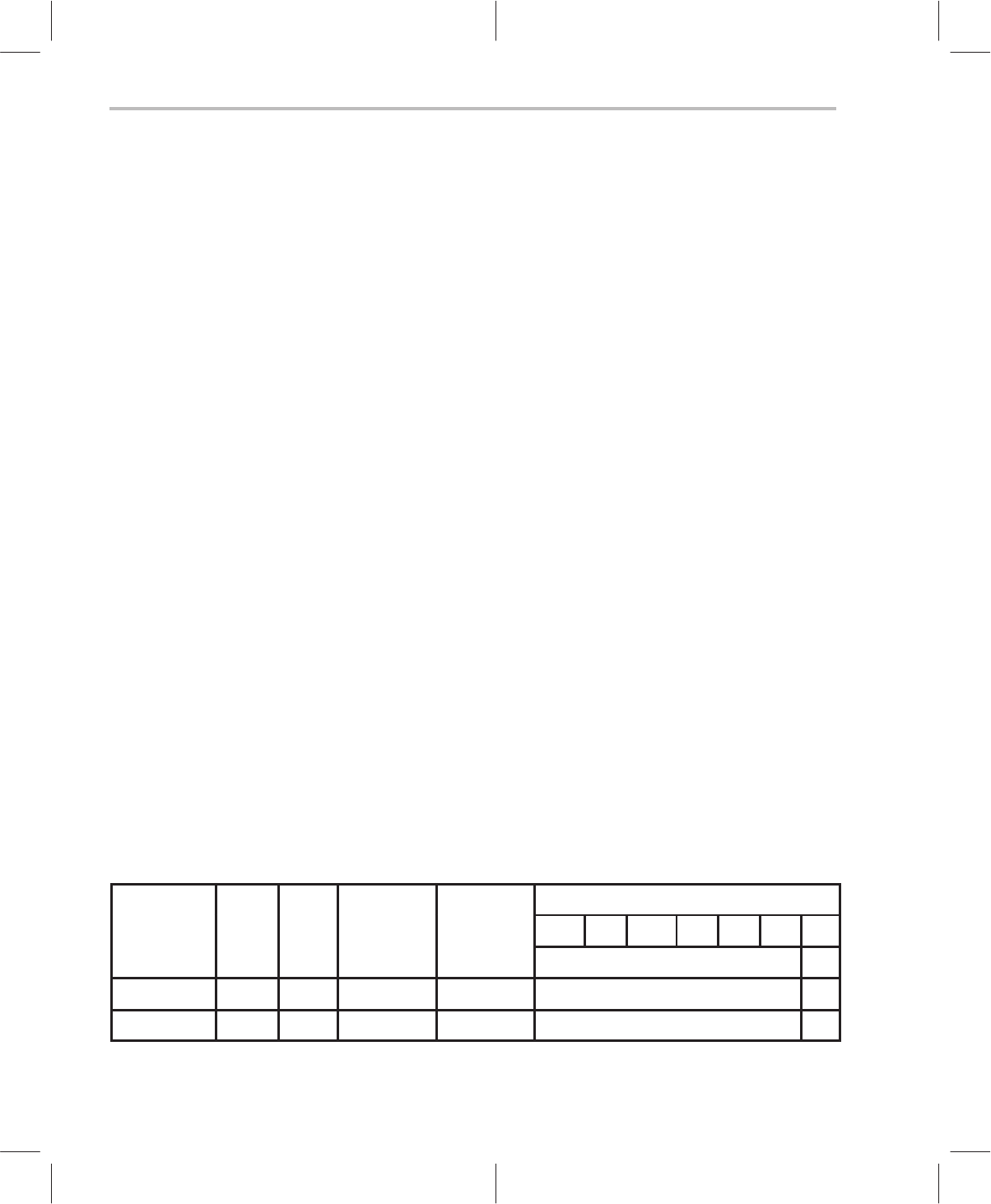
Table 4–7. Flag Addressing Field {flagadrs} for Certain Flag Instructions (Class 8a)
Flag
Repeat
{
flagadrs
} flag addressing mode encoding,
flagadrs
Flag
Addressing
Modes
Clocks
clk
Words
w
Repeat
Operation,
†
clk
Syntax 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
M
o
d
es
clk
w
c
lk
flag address bits g/r
Global 1 1 n
R
+2 *
dma6
dma6 0
Relative 1 1 n
R
+2 *R6+
offset6
offset6 1
†
n
R
is RPT argument


















