4.4.1 Options for Flow Direction
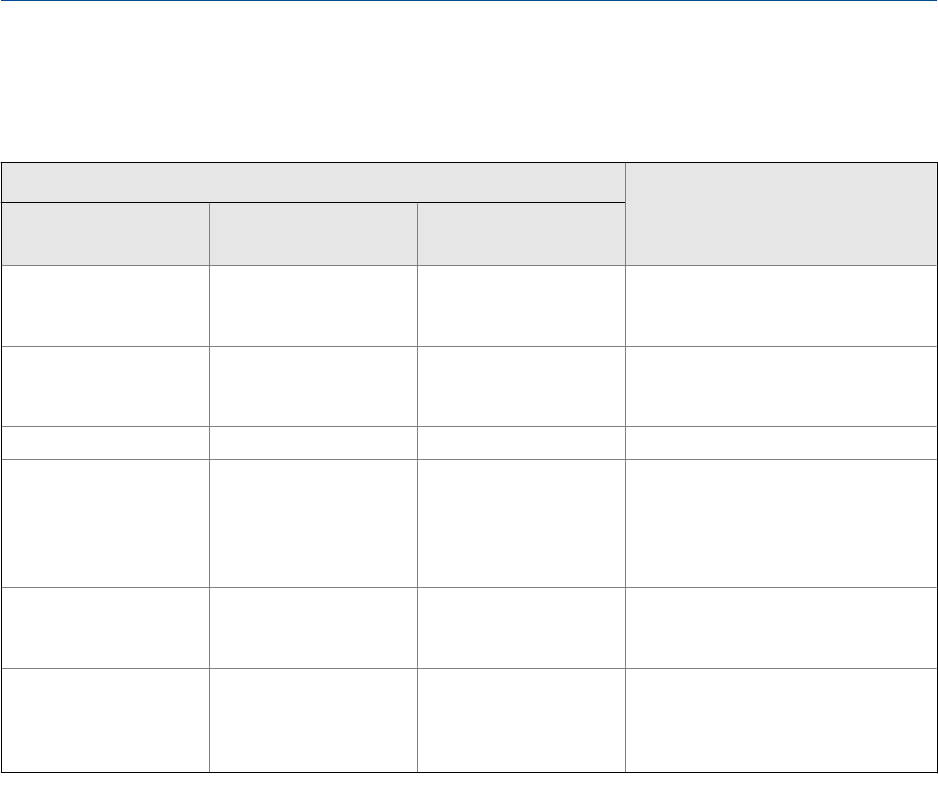
Options for Flow DirectionTable 4-5:
Flow Direction setting Relationship to Flow Direction ar-
row on sensor
ProLink II ProLink III Field Communicator
Forward Forward Forward
Appropriate when the Flow Direction
arrow is in the same direction as the
majority of flow.
Reverse Reverse Reverse
Appropriate when the Flow Direction
arrow is in the same direction as the
majority of flow.
Absolute Value Absolute Value Absolute Value
Flow Direction arrow is not relevant.
Bidirectional Bidirectional Bi directional
Appropriate when both forward and
reverse flow are expected, and for-
ward flow will dominate, but the
amount of reverse flow will be signifi-
cant.
Negate Forward Negate Forward Negate/Forward Only
Appropriate when the Flow Direction
arrow is in the opposite direction from
the majority of flow.
Negate Bidirectional Negate Bidirectional Negate/Bi-directional
Appropriate when both forward and
reverse flow are expected, and reverse
flow will dominate, but the amount of
forward flow will be significant.
Effect of Flow Direction on mA outputs
Flow Direction affects how the transmitter reports flow values via the mA outputs. The mA
outputs are affected by Flow Direction only if mA Output Process Variable is set to a flow
variable.
Flow Direction and mA outputs
The effect of Flow Direction on the mA outputs depend on Lower Range Value configured for
the mA output:
• If Lower Range Value is set to 0, see Figure 4-1.
• If Lower Range Value is set to a negative value, see Figure 4-2.
Configure process measurement
Configuration and Use Manual 41