61
Basic functions
** Musical data (MIDI RPN data) can be used to
change the starting settings during playback.
For details on control changes, refer to p.223 in the
Parameter Guide.
Patterns
There are two types of patterns: preset patterns and
user patterns.
• Preset patterns: Patterns suitable for drum tracks
are preset in internal memory, and can be selected
for any song.
• User patterns: Each song can have up to 100
patterns. When using a pattern in a different song,
use the page menu commands “Copy Pattern” or
“Copy From Song” etc. to copy the pattern. The
pattern length can be specified in units of a
measure.
Each pattern consists of musical data for one track. It is
not possible to create patterns that contain multiple
tracks.
These patterns can be used as track musical data by
being placed in a track (page menu command “Put to
Track”) or copied to a track (page menu command
“Copy to Track”). Alternatively, you can use a pattern
with the RPPR function of a song.
As track musical data of a song
Phrases that are used repeatedly in a song can be
recorded as patterns.
When you place (“Put to Track”) such a pattern in a
song, the musical data of that pattern will be recalled
and played when playback reaches the measure in
which the pattern was played. When using a phrase or
rhythm that occurs repeatedly, you can make more effi-
cient use of memory by creating a pattern and placing
it in multiple locations of the song, rather than actually
recording the same data directly to each location of the
song. However, be aware that if you modify the pat-
tern itself, the playback will be affected for all mea-
sures at which the pattern had been placed.
If you copy (“Copy to Track”) a pattern to a track of the
song, the playback data will be recorded on the track
just as if you had recorded it onto the track in the first
place. This will occupy more memory than if you use
“Put to Track,” but you will be able to edit each loca-
tion of data independently without affecting other
locations, just as when editing normal track data.
The RPPR (Realtime Pattern Play/Recording)
function:
For each song, you can assign patterns to each note of
the keyboard, and play notes on the keyboard to play-
back or record patterns in realtime.
Cue List
A cue list allows you to playback multiple songs in
succession. The TRITON allows you to create 20 cue
lists. Each cue list allows you to connect a maximum of
99 songs in any order, and to specify the number of
times that each song will repeat.
Each unit in a cue list is called a “step,” and each step
contains a song number and the number of repeats.
For example, a song consisting of an introduction, mel-
ody A, melody B, bridge, solo backing, and ending
could be created using a separate song for each unit.
Then you could use a cue list to play the introduction
twice, melody A four times, melody B four times, the
break twice, melody A four times, ... etc. to create the
completed song. When you will need to change the
structure of the song, the cue list function provides an
efficient way to do so.
The page menu command “Convert to Song” lets you
convert the two or more songs in a cue list into a single
song. This allows you to use a cue list to create the
backing, then convert the cue list into a song and add
solo phrases on unused tracks.
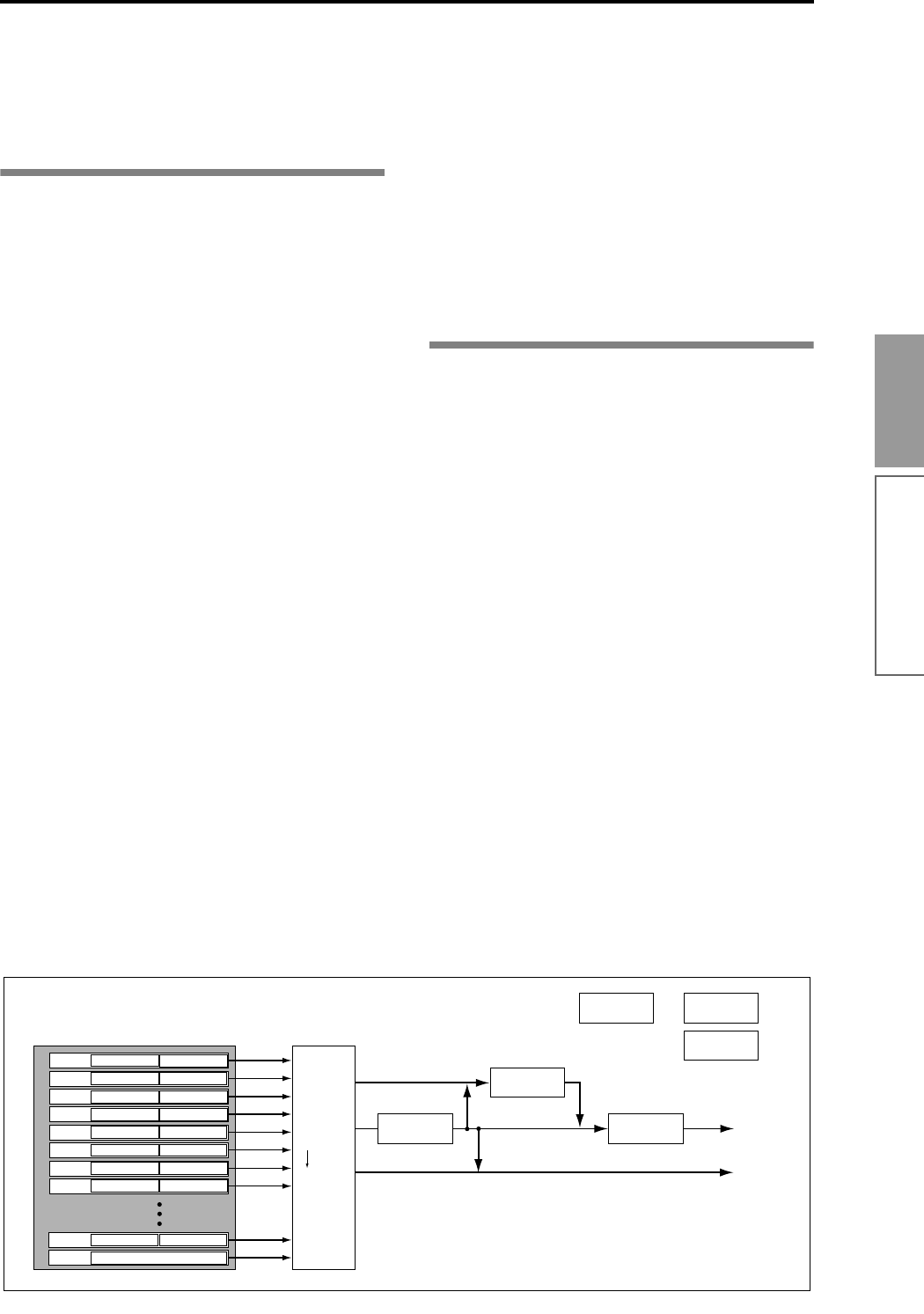
Insert Effect 1 ... 5 : P8
AUDIO OUTPUT
L/MONO, R
Master Effect 1, 2 : P9
AUDIO OUTPUT
INDIVIDUAL 1,2,3,4
MasterEQ : P9
Controller Setup : P4- 4
Arpeggiator : P7
Routing : P8-1
Track
Insert Effect
Master Effect
Individual Outputs
Track 1
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 2
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 3
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 4
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 5
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 6
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 7
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 8
Setup parameters
Musical data
Track 16
Setup parameters
Musical data
Master Track
Tempo, time signature data
Pattern U00 ... U99
RPPR Setup
: P6
Sequencer mode


















