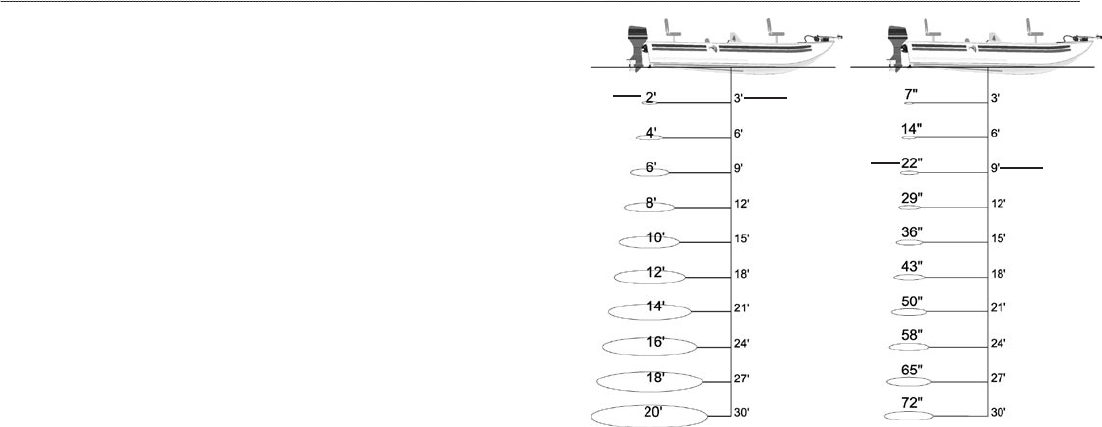
Transducer Coverage
The area covered by the transmitted sound waves is determined
by the cone angle of the transducer and the water depth. The wide
cone angles (40°) associated with low frequencies (50 kHz) provide
a large coverage area for finding fish within a coverage width that
is approximately 2/3 of the water depth. However, this also means
that wide cone angles produce less bottom detail and resolution. As
shown in the drawing on the near right, the 40° cone angle produces
a coverage area of approximately a 20-foot diameter circle at a 30-
foot depth.
The narrow cone angles (10°) associated with the high frequencies
(200 kHz) provide better bottom resolution and crisper detail, but
cannot show a large coverage area for finding fish. The 10° cone
angle provides a coverage width that is approximately 2/10 of the
water depth. As shown in the drawing on the far right, the 10° cone
angle produces a coverage area of approximately a 6-foot diameter
circle at a 30-foot depth.
Dual frequency mode combines both frequencies to get the best
coverage area and contour/depth readings.
40° Cone Angle (50 kHz)
Coverage
Diameter
Depth
10° Cone Angle (200 kHz)
Coverage
Diameter
Depth
GPSMAP 296 Pilot’s Guide 129
SETTING UP AND USING SONAR > UNDERSTANDING SONAR


















