Page 62 - IP Routing The Configuration Tree Functions
IP Routing
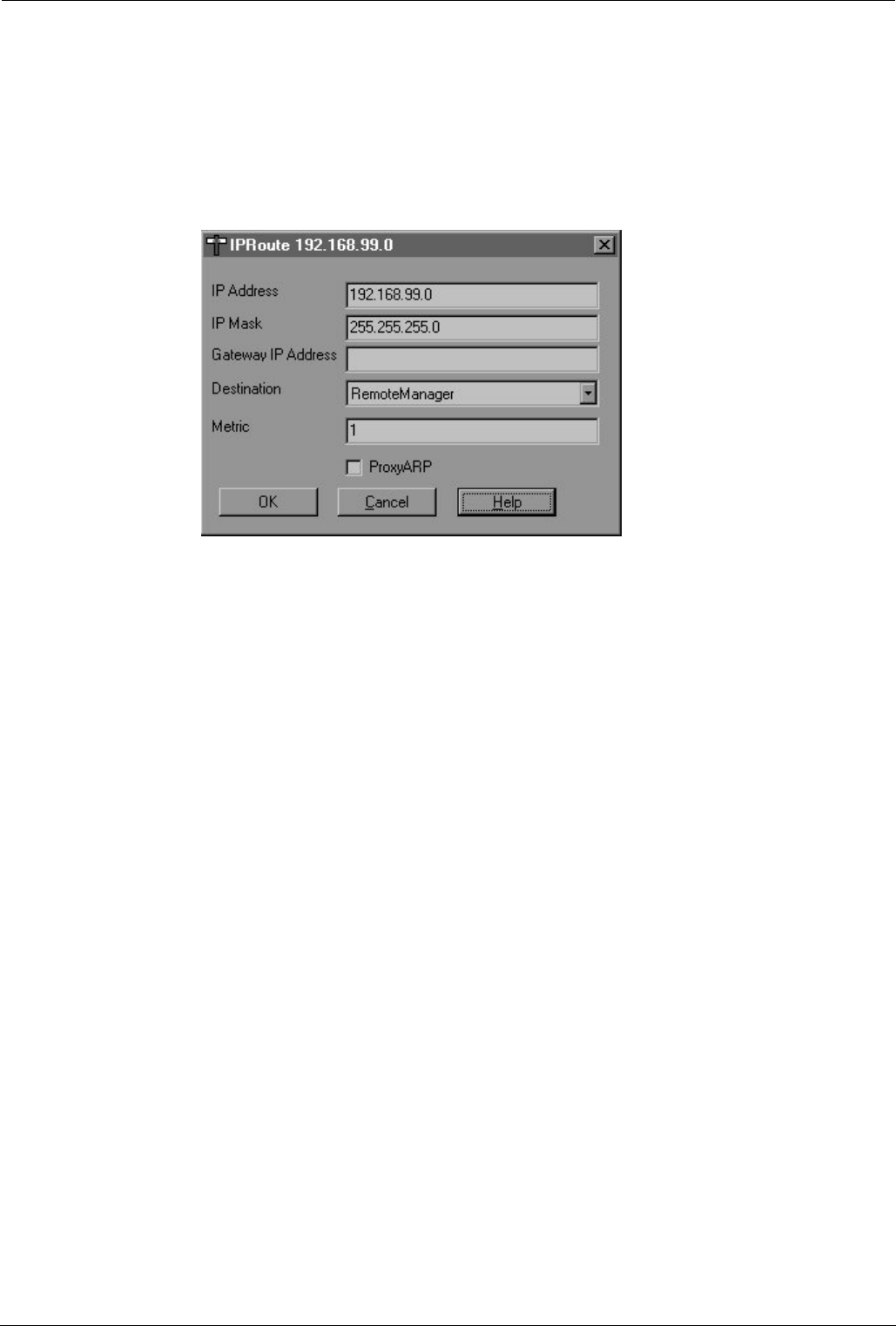
The IP Routing Form is used for setting-up routing for the IP network. When a
user sets up a call to an external service, data on the local subnet for the remote
IP Address must be correctly routed to the particular Service. A series of values
can be specified against which the addresses of data packets are compared.
Data are routed to a specified Destination if a match is found, the Destination
being one of a list of configured services or a default of LAN1, the local subnet -
this is used for packets with no address match, i.e. to confine internal traffic to the
local subnet.
IP Address: Either a specific IP address or, if left blank, the broadcast address
255.255.255.255. If a particular address is specified, any packets with a
destination address matching this are delivered to the selected Destination. If the
broadcast address is used, the system sends all packets to the chosen
Destination. Any other addresses are checked in turn against the Mask and
Gateway addresses to see if they match.
IP Mask: An IP Address Mask can be specified. Any incoming packets within the
mask are then routed to the selected Destination.
Gateway IP Address: Used to specify a Gateway on the local LAN, i.e., another
router, its IP Address can be specified here and all matching packets are sent to
it (see also Metric below).
Destination: This allows a Service name to be selected from a pull-down list of
all defined Services. There is a default destination, LAN1 (the local LAN), which
means that any packets with no address matches remain on the local subnet.
Metric: A numeric value (default 1) indicating the number of “hops” in the route.
Each time a data packet passes through a router, the “hop” count is incremented
by 1. Some protocols impose a maximum hop count, after which the packet is
discarded. The default value need only be increased if the ultimate destination
involves additional routers.
Proxy ARP: If the box is ticked, the system acts as an Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP) server, and can respond to ARP requests for the specified
network. ARP resolves the IP address of a host device into the physical address
of it's network adapter.
Page 62 - The Configuration Tree Functions INDeX IPNC Cassette Administration Manual
IP Routing 38DHB0002UKDD – Issue 7 (22/11/02)


















