Software Upgrading and Installation Installation of a New System - Page 13
Installation of a New System
At initial start up or reset, the IPNC searches for an IP address from any available
DHCP server. If an IP address is found, the IPNC adopts a DHCP client mode
and accepts the address. Alternatively, an IP address is not found, the default IP
address is loaded and the IPNC adopts DHCP server mode. See The Boot
Process on page 7.
The IPNC may be connected, via a hub, to an existing LAN that uses either static
or dynamic addressing.
It is simpler to ensure that the manager PC is set to automatic IP addressing
(using DHCP) before proceeding. See Dynamic IP Addressing on page 14 and
Addressing on the Local Subnet on page 33.
Static IP Addressing
The following paragraphs detail the configuration requirements for static IP
addressing of the Administration PC which will be used to configure the IPNC.
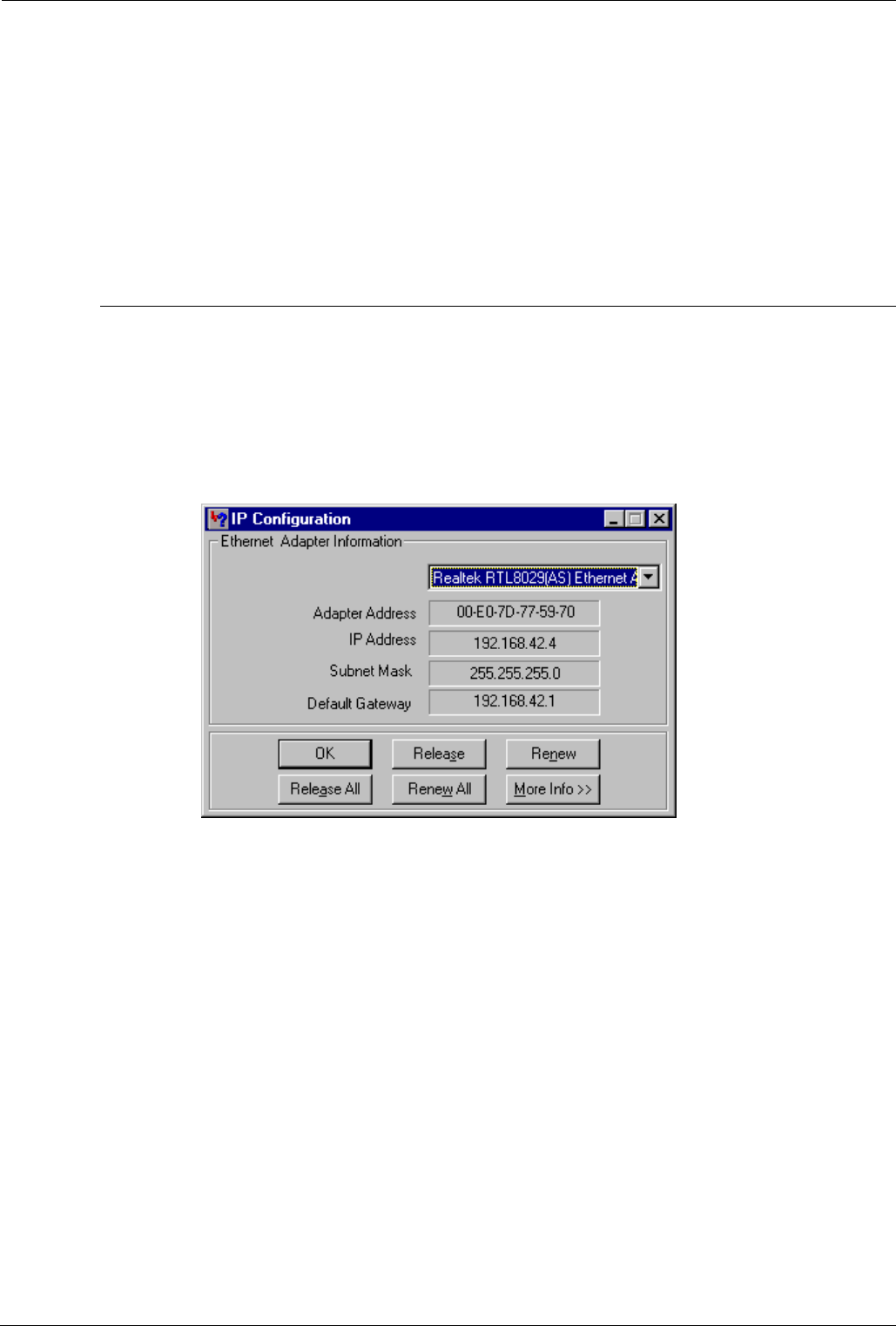
To examine the IP configuration, use Start/Run/winipcfg (Windows 95/98). On
win 2000/NT/XP use the DOS command ipconfig; this command is used to
control IP address allocation/status.
A screen similar to the following example will be displayed:
For an explanation of the IP terms used in this and other menus, see Appendix C:
Overview of IP Routing on page 125.
In the example shown above, the Release and Renew buttons are inactive as
static IP addressing is in force. If the Manager PC is connected to a network with
static addressing, make a note of the IP address as you will need it later during
the configuration procedure.
A PC with static addressing will fail to communicate with the IPNC if it has been
configured for a different network. If your PC fails to communicate with the IPNC
at the beginning of the procedure, check that it is set to automatic addressing
(see page 14).
INDeX IPNC Cassette Administration Manual Software Upgrading and Installation - Page 13
38DHB0002UKDD – Issue 7 (22/11/02) Installation of a New System