Page 106 - Part 2 Voice Over IP How Do I?
Configuring VoIP
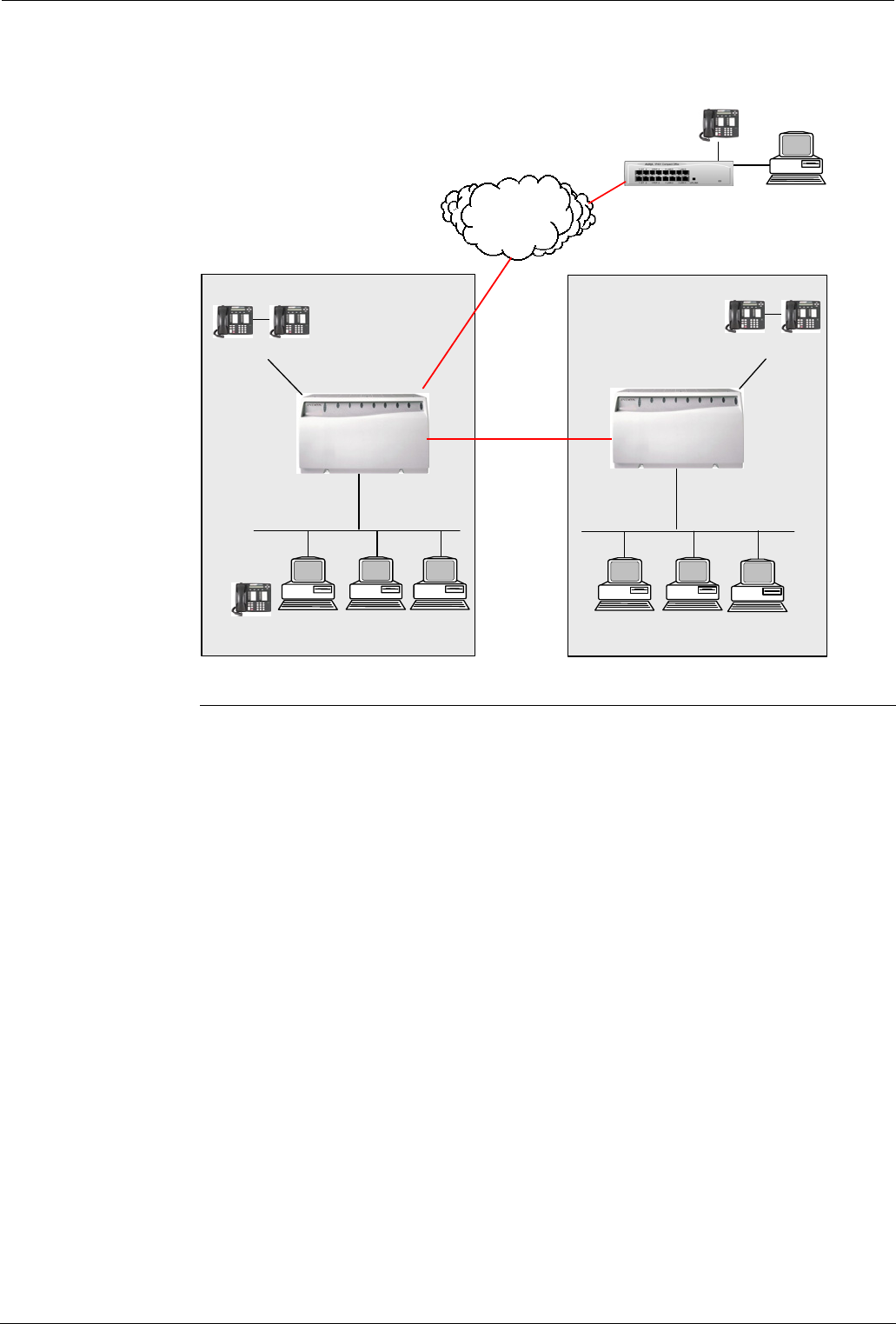
The following example of a VoIP network features INDeX to INDeX as well as a
Home Office / Small Office. This allows VoIP calls to support 'user to user'
features that are normally specific to DPNSS.
IP Network 1
INDeX and IPNC
(emulating DPNSS)
Site 1 (Node 62)
VoIP Trunk
LAN IP Address
192.168.200.10/24
Gateway 1
IP Endpoint
(Extn 4321)
IP Network 2
Site 2
LAN IP Address
192.168.50.1/24
INDeX and IPNC
Gateway 2
Site 1 (Node 63)
Extn 3000 - 3100
ISDN
Site 1
Extn 2000 - 2100
IP Office 401
Home Office/Small Office
INDeX to INDeX VoIP Trunking
The INDeX IP Networking cassette (IPNC) allows the use of the data Wide Area
Network to make desk to desk voice calls between INDeX's. Since leased lines
typically have a fixed cost, voice traffic essentially travels for free, courtesy of the
data infrastructure. The IPNC uses voice compression technology to make the
most of available network capacity. Using industry standard compression (G.
723.1 and G.729a ) up to 20 voice calls can be made simultaneously.
Recent releases of INDeX software introduce the ability to packetise our DPNSS
and INDeX-Net feature set over an IP trunk. This means that VoIP no longer has
to be lacking in functionality with nearly 30 facilities available over an IP trunk.
This positions INDeX in a very strong networking position with the ability to
network over traditional private voice circuits, dial up, ISDN circuits and now IP
circuits.
VoIP can be implemented either by connecting the leased line directly to the
INDeX, or by using existing leased line routers. Connecting the leased line
directly to the INDeX is the simplest and most secure solution - the IPNC takes IP
data from the LAN and combines it with INDeX voice traffic for delivery over the
leased line. Each leased line can operate at speeds of up to 2Mbps.
Page 106 - How Do I? INDeX IPNC Cassette Administration Manual
Part 2 Voice Over IP 38DHB0002UKDD – Issue 7 (22/11/02)


















