Appendix C: Overview of IP Routing Network Address Translation (NAT) - Page 129
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT is a mechanism that allows IP addressing scheme to be hidden from any
TCP/IP network to which TCP/IP traffic is routed. For example, an established
network may be using a numbering scheme that is not consistent (non-compliant)
with the Internet. There are many cost-effective ISP but they want you to use a
different IP address. By using NAT between your machine and their network
everyone is satisfied, and no need to renumber your network. An additional
benefit is that all your machines can use the NAT facility and access the Internet
via the one address.
The IPNC Network Address Translation (NAT) functionality allows an IP address
or network (Internal) to be translated to single globally unique IP address
(external). In this way non-compliant addressing schemes may be used in
conjunction with Internet access.
– Single IP Address Internet connectivity. Multiple-PC can simultaneously
access the Internet via a single ISP account.
– Network address translation (NAT) allows an existing TCP/IP network-
addressing scheme to be used for connection to the Internet.
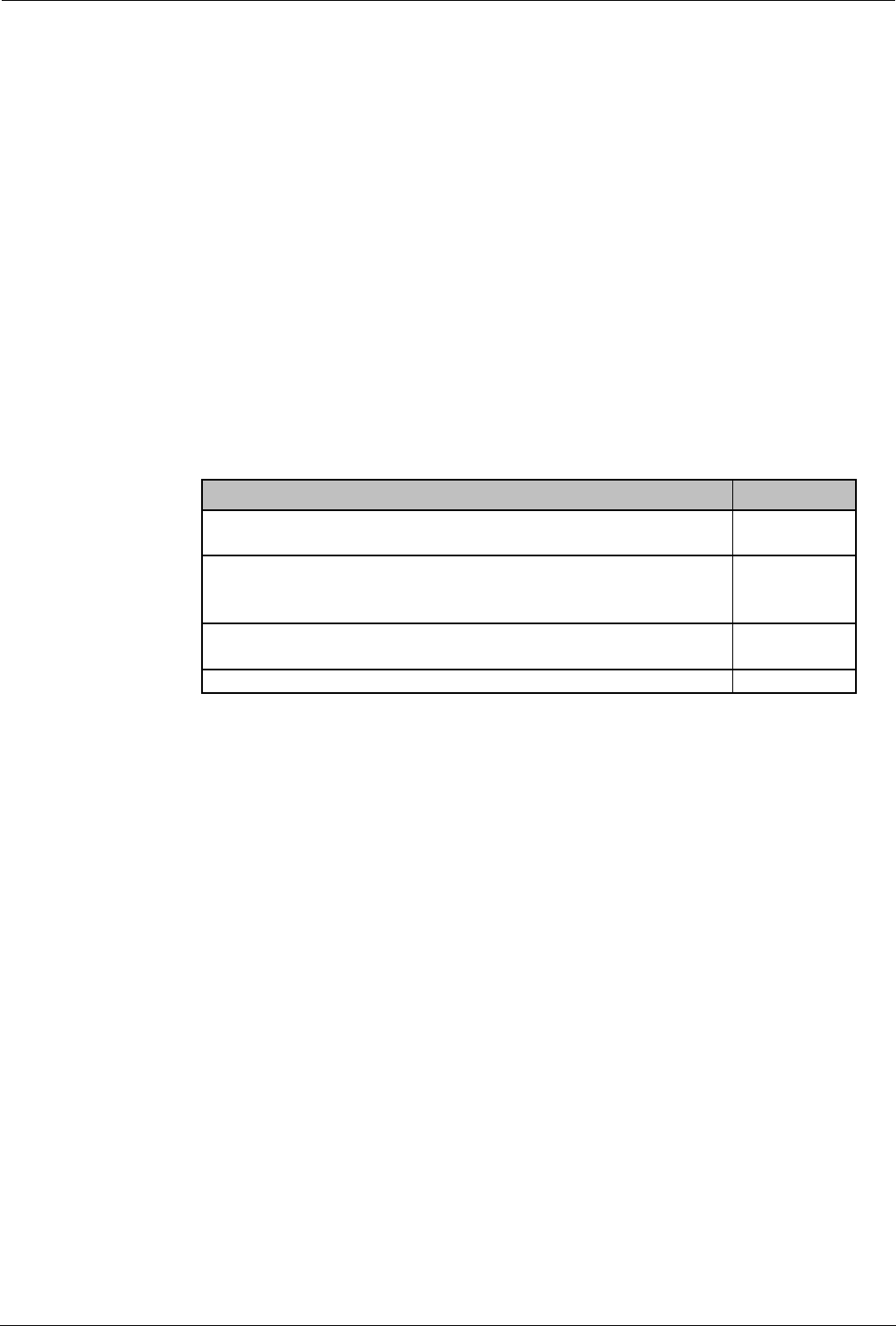
NAT is automatically enabled on the IPNC under the following connection
scenarios:
Condition NAT status
Service / Advanced IP Mask = 255.255.255.255 On
The IPNC is offered and accepts an IP address during the
IPCP stage of PPP link establishment.
Service / Advanced IP Address = Blank
On
A mask other than 32-bit is assigned to the Service.
Disabled.
A Service is configured with the same name as a User Disabled.
INDeX IPNC Cassette Administration Manual Appendix C: Overview of IP Routing - Page 129
38DHB0002UKDD – Issue 7 (22/11/02) Network Address Translation (NAT)


















