Page 128 - Firewall Rules Appendix C: Overview of IP Routing
Firewall Rules
1. The default behaviour for incoming session is to block, unless a specific
entry exists to forward the session.
2. ICMP are blocked for incoming sessions by default may not be forwarded
3. Non-default protocols are forwarded for outgoing connection unless a
specific entry exists to drop the session
4. When an Entry match offset is set to 0 all data in IP header is matched
(effectively this don’t care mechanism)
5. When an Entry is configured with the protocols set to 0 all protocols are
matched (effectively this is a don’t care)
6. The firewall engine searches the entry list only until the first match is found.
7. To aid the efficiency of the firewall engine matches are not performed on
entries that have the same action as the generic. For example, if FTP is to be
dropped and a further entry exists, that entry will not be checked before the
packet is dropped.
8. If a packet contains an unauthorised request such as a banned Web site, the
IPNC immediately replies to the packet's originator with a protocol exchange
that terminates the transaction, effectively blocking the request.
9. The Action are outgoing (Out), incoming (In), Bothway or not at all (Drop).
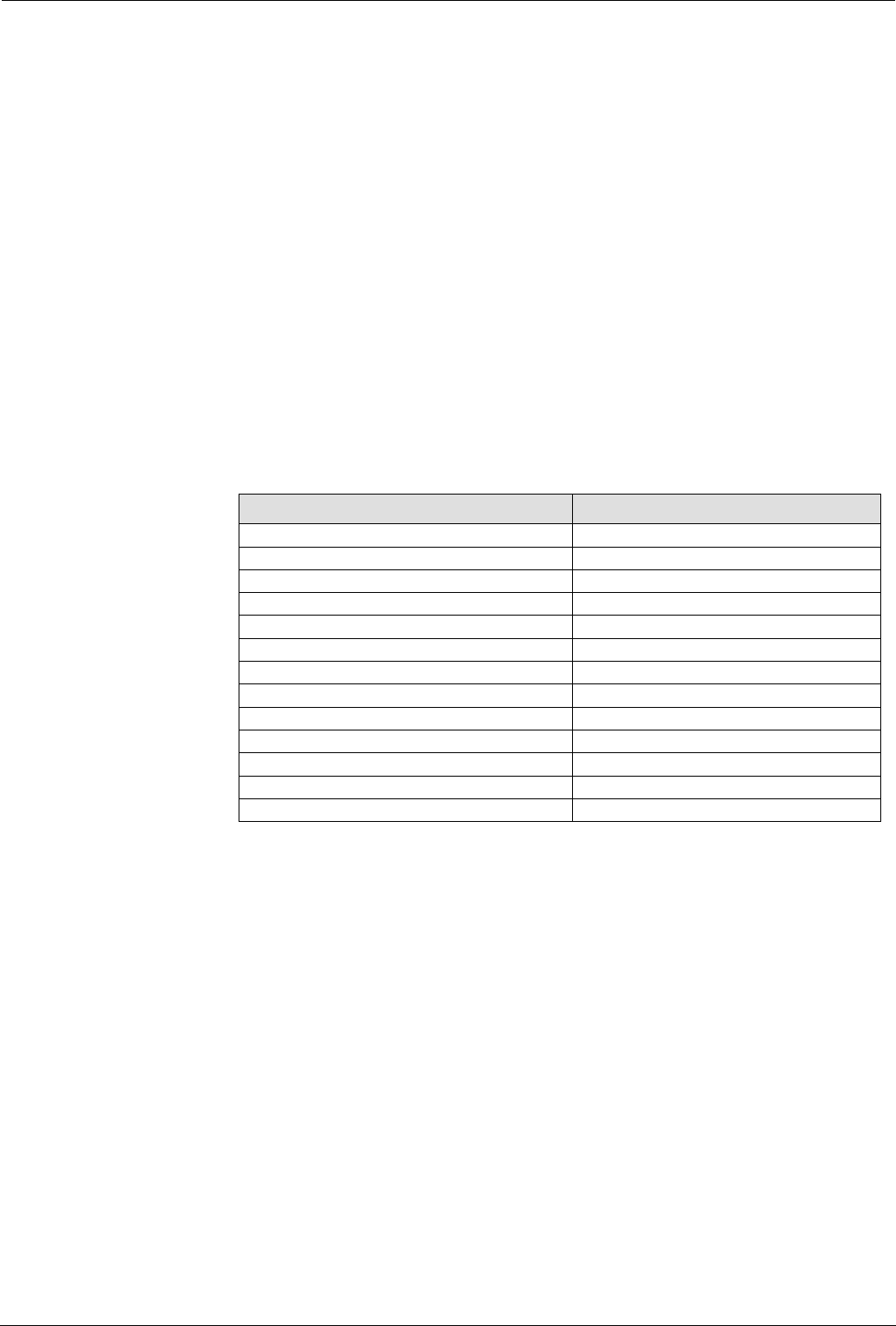
The default protocols that can be easily configured this way are:-
Generic Protocol Description
FTP File Transfer Protocol
Telnet 23/tcp Remote Terminal Login
SMTP 25/udp Email delivery
POP3 Email reception
DNS Domain Name Server
Time Time update protocol
Gopher
Finger 79
HTTP dec 80 Web Access
NNTP Network News
SNMP Management
IRC Internet Relay Chat
PPTP Point-to Point-Tunnelling Protocol
10. Multiple firewall profiles may be created, a profile may be assigned to a
service for outgoing call or for User incoming calls. A firewall configuration
may be assigned to one or may services or user configuration.
Page 128 - Appendix C: Overview of IP Routing INDeX IPNC Cassette Administration Manual
Firewall Rules 38DHB0002UKDD – Issue 7 (22/11/02)


















