UHF (7640) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
5B-9
November 1998
Part No. 001-7600-001
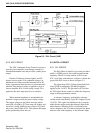
Part of the AF signal from pin 9 of FM IF circuit
IC1 is applied to pin 24 of level controller IC12. This
device allows the CPU to control the squelch threshold
level. The level-controlled output signal on pin 23 is
applied to IC1, pin 8 which is the input of an internal
filter (see Figure 5-4). Noise frequencies are passed
and then fed out on pin 7 and also applied to an inter-
nal noise detector.
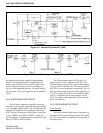
The detected noise signals are rectified and fed
out on pin 13 without smoothing. The noise signal
(NOIS) is then applied to pin 19 of CPU IC1. The
CPU analyzes the noise condition and outputs the
RMUT signal via I/O expander IC13. This signal con-
trols AF mute switch IC11a (see Figure 5-5).
Call Guard (CTCSS/DTCS) Operation
The tone Call Guard squelch circuit detects AF
signals and opens the squelch only when receiving a
signal containing a matching subaudible tone or code
(CTCSS or DTCS). When tone squelch is in use and a
signal with a mismatched or no subaudible tone is
received, the tone squelch circuit mutes the AF signals
even when noise squelch is open.
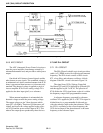
A portion of the audio signal from amplifier IC7b
passes through low-pass filter Q5 in the front unit to
remove voice signals. It is then applied to CPU IC1 on
pin 97 via the “CTCIN” line. The CPU detects the
CTCSS or DTCS signaling and controls the AF mute
switch via I/O I/O expander IC13.
5.6 UHF TRANSMITTER CIRCUIT
5.6.1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies the
microphone audio signal to the level required by the
modulation circuit and also provides pre-emphasis.
The microphone audio signal is amplified by
IC8b and limited by IC8a. Pre-emphasis is provided
by R152 and C180. The signal is then fed to splatter
filter IC7a and then to pin 11 of switching circuit
IC11.
The output signal from IC11 on pin 10 is fed to
pin 16 of level controller IC12. This device provides
deviation control and is also used in the receive mode
to provide volume control. The level controlled output
on pin 15 is fed to pin 3 of switching circuit IC11. The
switched output (MOD) on pin 4 is then applied to the
PLL circuit (D21) where it frequency modulates the
transmit signal.
Narrow band/wideband switch Q35 is connected
to the input of the splatter filter IC7a and switched by
the “NWC” signal from the I/O expander IC13. When
“NWC” is high, Q35 shifts the filter cut-off frequency
for narrow band deviation selection.
5.6.2 MODULATION CIRCUIT
The microphone audio signal modulates the fre-
quency of transmit VCO Q25. The “MOD” signal
from switch IC11, pin 4 changes the reactance of
diode D21 and this modulates the frequency of trans-
mit VCO Q25. The modulated VCO signal is ampli-
fied by buffer amplifiers Q28 and Q30 and applied to
the transmit driver circuit (Q21).
5.6.3 TRANSMIT DRIVER CIRCUIT
The transmit driver circuit amplifies the VCO
oscillating signal to the level required by the power
amplifier module. The RF signal from buffer amplifier
Q30 passes through the T/R switch D18 and is ampli-
fied by the buffer amplifiers Q21, Q20, and driver
Q19. The signal is then applied to the power amplifier
module IC5.
5.6.4 POWER AMPLIFIER MODULE
The power amplifier module amplifies the driver
signal to the output power level. The RF signal from
the driver Q19 is applied to the power module which
produces 35 watts of output power at the antenna jack.
The amplified signal is fed through antenna
switching circuit D3, a low-pass filter and APC detec-
tor, and is then applied to the antenna jack. The collec-
tor voltage of driver Q19 and the control voltage on
pin 2 of the power module IC5 come from APC tran-
sistors Q17 and Q18. Transmit switch Q16 turns off
Q17 and Q18 when the transmitter is disabled.