Design Guide for the Polycom SoundStructure C16, C12, C8, and SR12
A - 4
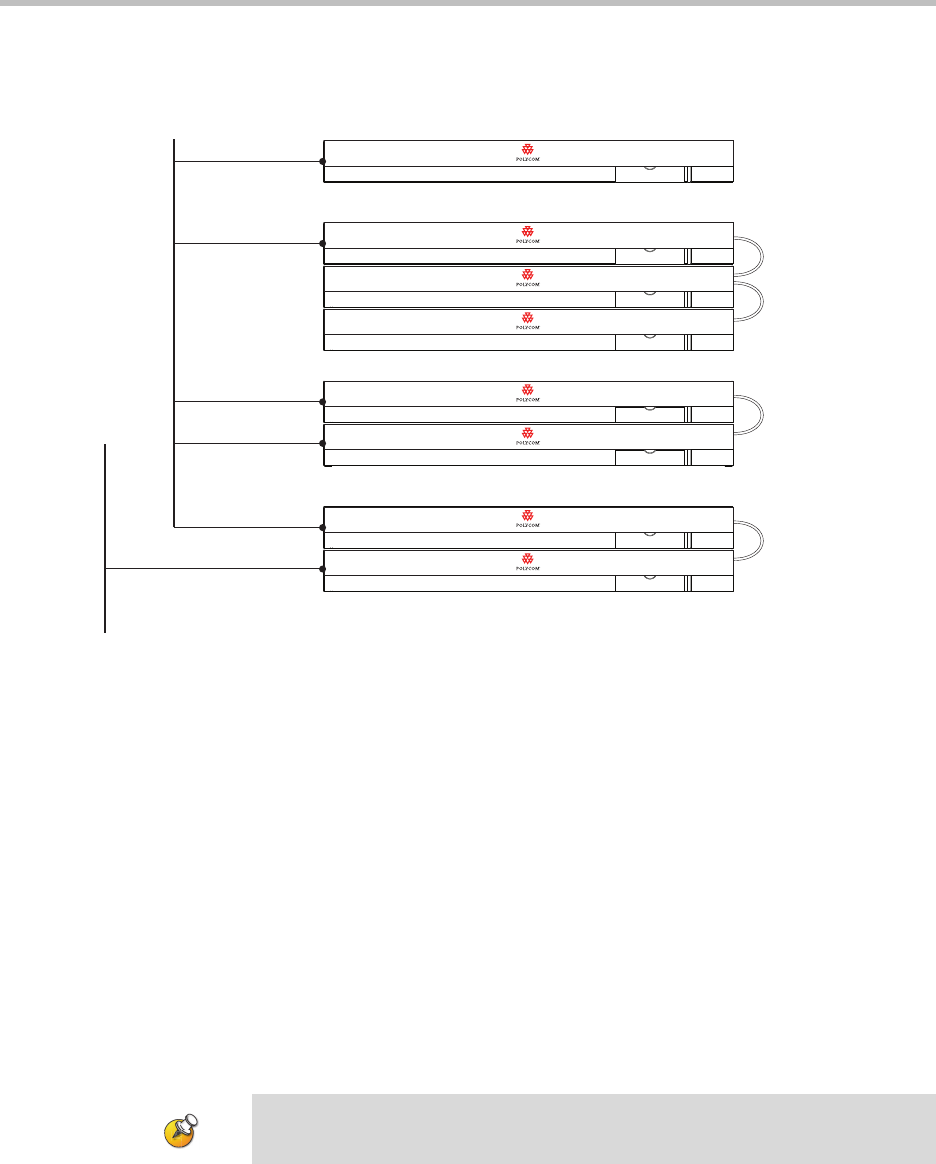
used to connect the SoundStructure devices to more than one network.
Multiple network connections can be on the same network or on different
subnets as shown in the following figure.
The SoundStructure Ethernet interface can be configured to have either a static
IP address or can accept a dynamic IP address from a DHCP server. By default
the SoundStructure products will accept an IP address from a DHCP server.
Virtual Channels
As described in Chapter 3, a virtual channel is a representation of an
individual physical input or output channel. A virtual channel may also be a
stereo pair of physical inputs or output channels. The virtual channel name
that is created when the virtual channel is defined by the A/V designer is used
to refer to that particular input or output instead of using the physical channel
number. For example, the designer would define the virtual channel “Podium
mic” that is connected, for example, to input physical channel 9 and then refer
the virtual channel as “Podium mic”. Once a virtual channel is defined, it is
always used to reference that particular signal or signals.
.
SoundStructure C16
TM
SoundStructure C16
TM
Ethernet
192.168.1
Ethernet
172.22.2
.101
SoundStructure C16
TM
OBAM Link
OBAM Link
SoundStructure C16
TM
.102
.103
SoundStructure C16
TM
OBAM Link
SoundStructure C16
TM
.104
.122
SoundStructure C16
TM
OBAM Link
SoundStructure C16
TM
.100
Warni ng
The Virtual channel name is case-sensitive: “Podium Mic” and “PODIUM mic”
would represent two different virtual channels.


















