APPENDICES
APPENDICES-20
M32R-FPU Software Manual (Rev.1.01)
APPENDIX 5
Appendix 5 IEEE754 Specification Overview
Appendix 5.2 Rounding
The following 4 rounding modes are specified by IEEE754.
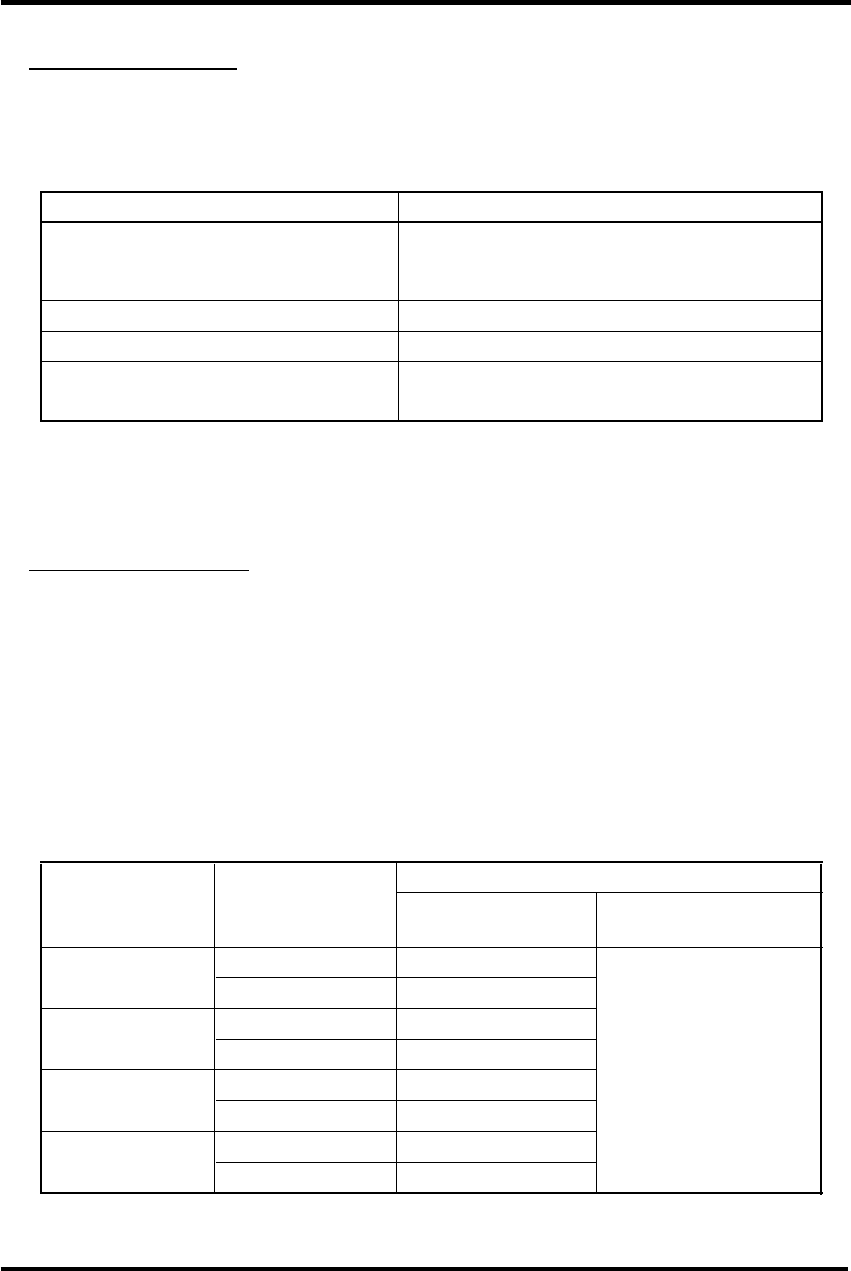
Appendix Table 5.2.1 Four Rounding Modes
Rounding Mode Operation
Round to Nearest (default) Assuming an infinite range of precision, round to the best
approximation of the result. Round an interval arithmetic
result to an even number.
Round toward –Infinity Round to the smaller magnitude of the result.
Round toward +Infinity Round to the larger magnitude of the result.
Round toward 0 Round to the smaller in magnitude of the absolute value
of the result.
• “Round to Nearest” is the default mode and produces the most accurate value.
• “Round toward –Infinity,” “Round toward +Infinity” and “Round toward Zero” are used
for interval arithmetic to insure precision
Appendix 5.3 Exceptions
IEEE754 allows the following 5 exceptions. The floating-point status register is used to
determine whether the EIT process will be executed when an Exception occurs.
(1) Overflow Exception (OVF)
The exception occurs when the absolute value of the operation result exceeds the
largest describable precision in the floating-point format. Appendix Table 5.3.1 shows
the operation results when an OVF occurs.
Appendix Table 5.3.1 Operation Result due to OVF Exception
Result
Rounding Mode Sign of Result when the OVF EIT when the OVF EIT
processing is masked processing is executed
–Infinity + +MAX round (x2 ^ -a)
––Infinity a = 192 (single-precision)
+Infinity + +Infinity a = 1536 (double-precision)
––MAX
0 + +MAX
––MAX
Nearest + +Infinity
––Infinity
Note : • When the Underflow Exception Enable (EU) bit (FPSR register bit 18) = "0"
• When the Underflow Exception Enable (EU) bit (FPSR register bit 18) = "1"


















