EXPERT
91
En
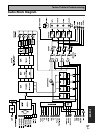
Techno Tidbits & Problem-solving
5.1 channel
4 channel analog
Dolby
Digital
Dolby Digital for movie
Soundtracks using linear PCM audio generate too much
data for multichannel use. Dolby Digital technology was
developed in response to the need for efficient
multichannel digital sound. It uses masking technology and
Adaptive Transform Coding, resulting in no audible loss of
sound quality. In the present age of digital sound Dolby
Digital is a standard audio format for DVD and has been
adopted by HDTV broadcasts throughout the USA.
Dolby
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is a discrete digital surround format used for multichannel surround sound. It was developed after
the Dolby Surround System and Dolby Pro Logic Surround System. Dolby Digital is a high quality digital sound
format that is used by many theatrical film releases.
Other features include:
1) Downmixing on playback for compatibility with mono,
stereo, Dolby Pro Logic and 5.1 channel audio.
2) A wide range of bitrates and channels.
3) Decoding dynamic range information and adjusting the
dialog level in the soundtrack (called Dialog Normalization,
see below for more information).
The advantages of the Dolby Digital system of encoding
allow it to maintain its high quality sound while at the same
time being very flexible, with the ability to handle many
different types of soundtracks.
Dialog Normalization
When a Dolby Digital soundtrack is played back the Dialog Normalization function of the amplifier activates auto-
matically. Dialog Normalization is a Dolby Digital function that establishes the average dialog level for the program
source being played. If the amplifier's level does not match the average dialog level, first you see "DIAL NORM"
and "OFFSET +4 dB" (as an example) appear in the amplifier's display. In this example, the number +4 dB is the
difference between the amplifier's gain structure and the Dolby Digital average dialog level. To match the average
dialog level, subtract or add the OFFSET level. For example, if the OFFSET level is +4 dB, the amplifier's output is
4 dB over the average recorded level.