58
En
13 Additional Information
Glossary
Analog audio
An electrical signal that directly represents sound. Compare
this to digital audio which can be an electrical signal, but is
an indirect representation of sound. See also Digital audio.
Aspect ratio
The width of a TV screen relative to its height. Conventional
TVs are 4:3 (in other words, the screen is almost square);
widescreen models are 16:9 (the screen is almost twice as wide
as it is high).
Chapter (DVD only)
Just as a book is split up into several chapters, a title on a DVD
disc is usually divided into chapters. See also Title.
Digital audio
An indirect representation of sound by numbers. During
recording, the sound is measured at discrete intervals (44,100
times a second for CD audio) by an analog-to-digital
converter, generating a stream of numbers. On playback, a
digital-to-analog converter generates an analog signal based
on these numbers. See also Sampling frequency and Analog
audio.
Dolby Digital
A surround sound system developed by Dolby Laboratories
containing up to six channels of digital audio (front left and
right, surround left and right, center and low-frequency
channels). See also DTS.
DTS
A surround sound system developed by Digital Theater
Systems as an alternative to Dolby Digital. DTS discs contain
up to eight channels of digital audio. See also Dolby Digital.
Dynamic range
The difference between the quietest and loudest sounds
possible in an audio signal (without distorting or getting lost
in noise). Dolby Digital and DTS soundtracks are capable of a
very wide dynamic range, delivering dramatic cinema-like
effects.
MPEG video
The video format used for Video CDs and DVDs. Video CD uses
the older MPEG-1 standard, while DVD uses the newer and
much better quality MPEG-2 standard.
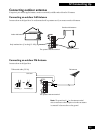
Optical digital output
A jack that outputs digital audio in the form of light pulses.
Connect components with optical digital jacks using a special
optical cord, available from good audio dealers.
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
The most common system of encoding digital audio, found
on CDs and DAT. Excellent quality, but requires a lot of data
compared to formats such as Dolby Digital and MPEG audio.
For compatibility with digital audio recorders (CD, MD and
DAT) and AV amplifiers with digital inputs, this unit can
convert Dolby Digital and MPEG audio to PCM. See also
Digital audio.
PBC (PlayBack Control) (Video CD only)
A system of navigating a Video CD through on-screen menus
recorded onto the disc. Especially good for discs that you
would normally not watch from beginning to end all at
once—karaoke discs, for example.
Regions (DVD only)
These associate discs and players with particular areas of the
world. This unit will only play discs that have compatible
region codes. You can find the region code of your unit by
looking on the rear panel. Some discs are compatible with
more than one region (or all regions).
Sampling frequency
The rate at which sound is measured to be turned into digital
audio data. The higher the rate, the better the sound quality,
but the more digital information is generated. Standard CD
audio has a sampling frequency of 44.1kHz, which means
44,100 samples (measurements) per second. See also Digital
audio.
Title (DVD only)
A collection of chapters on a DVD disc. See also Chapter.