MAX-CSE Web Interface
36
MAX-CSE/MAX-CSD10 Operation/Reference Guide
The following table lists the IP Settings page features that an administrator or other authorized user can
configure.
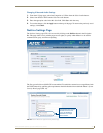
Changing the IP Settings
1.
From the IP Settings page and in the IP Address section, select between Dynamic and Static on the
IP radio button.
2. If you selected Static, enter the new IP Address and Subnet Mask settings, if necessary.
3. Enter the new Gateway setting, if necessary.
4. In the DNS Address section, enter the new Domain Suffix, Primary DNS, and Secondary DNS
settings in the appropriate fields, if necessary.
5. To save your changes, click the Accept button. To return to the previously saved entries, click
Cancel.
6. To submit the changes to the Master, click Reboot to reboot the MAX-CSE.
IP Settings Page Features
Feature Description
IP Address: This section allows the user/administrator to define the
communication and encryption parameters of the target Master.
• IP These radio boxes provide the option to select from either a DHCP or Static communication
mode on the MAX-CSE.
• DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) assigns IP Addresses from client stations
logging onto a TCP/IP network via a DHCP server.
• Static IP is a permanent IP Address that is assigned to a node in a TCP/IP network.
• Host • Allows the user to set the host name of the MAX-CSE.
• IP Address Allows a user to enter the IP Address or URL used by the current MAX-CSE.
Note: This is the same IP Address used by NetLinx Studio to communicate with the Master.
Target Master IP Address must be in IPv4 dot notation (ex: X.X.X.X).
• Subnet Mask Allows the user to set a subnetwork address to the MAX-CSE.
• Subnetwork mask is the technique used by the IP protocol to filter messages into a
particular network segment (Subnet).
• Gateway Allows the user to set a gateway value to the MAX-CSE.
• Gateway is a computer that either performs protocol conversion between different types of
networks/applications or acts as a go-between two or more networks that use the same
protocols.
DNS Address: This section allows the user/administrator to define the communication and encryption
parameters of the target Master.
• Domain Suffix Allows the user to set the unique name on the Internet to the MAX-CSE for DNS look-up.
• The unit belongs to the DNS domain.
• Primary DNS Allows the user to set the address of the primary DNS server used for host name lookups.
• DNS information must be in IPv4 dot notation (ex: X.X.X.X).
• DNS (Domain Name System) is software that lets users locate computers on a local
network or the Internet (TCP/IP network) by host and domain. The DNS server maintains
a database of host names for its domain and their corresponding IP Addresses.
• Secondary DNS • Allows the user to set the address of the secondary DNS server used for host name
lookups.
• DNS information must be in IPv4 dot notation (ex: X.X.X.X).