ELECTRO-VOICE
®
2.4 Rigging an Array with Boxes Using X-Line Dollies
Three dollies are available for transporting the X-Line loudspeaker systems. The actual array
rigging technique will vary depending on which dollies are used to transport the systems.
The Bottom Stacking Dolly can be used with the rectangular loudspeaker enclosures (Xvls, Xsub).
Up to four loudspeaker systems can be stacked on top of a single dolly. The enclosures all sit
upright as they would be arrayed. These dollies have sufficient clearance to allow the enclosures
to travel with both the front and rear rigging hardware attached to the loudspeaker systems. This
makes rigging set up and tear down extremely easy because the loudspeaker enclosures can be
moved in blocks of four units. The Downfill Stacking Dolly can be used with one downfill
enclosure (either the Xfil1 or Xfil2) and two Xvlt systems. The three loudspeaker systems are
stacked so that the enclosures all sit upright as they would be arrayed. The dollies are designed
to accommodate the slanted baffle of the Xfil1 and Xfil2 and the trapezoidal shell of the Xvlt
systems. These dollies have sufficient clearance to allow the enclosures to travel with both the
front and rear rigging hardware attached to the loudspeaker systems. Like the Bottom Stacking
Dollies, this makes rigging set up and tear down extremely easy because the loudspeaker
enclosures can be moved in blocks of three units.
The Front Dolly can be used with either the rectangular enclosures (Xvls or Xsub) or trapezoidal
enclosures (Xvlt). The front dolly attaches to the front of a single loudspeaker system covering the
grille and the enclosure front rigging track. This dolly allows the ease of moving one loudspeaker
enclosure at a time; however, the rigging cannot remain attached to the enclosure during
transport.
Because most arrays typically require more rectangular Xvls and Xsub systems than trapezoidal
Xvlt systems, it would be common in a large-scale touring situation for the rectangular boxes to be
transported on Bottom Stacking Dollies and trapezoidal and downfill boxes to be transported on
Downfill Stacking Dollies. However, some users prefer to transport the trapezoidal boxes on front
dollies. In cases where a venue will not accommodate the large bottom-stacked arrays and the
boxes must be individually handled, front dollies must be used.
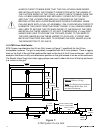
Figure 9 illustrates the technique used to construct a loudspeaker array with enclosures
transported on Bottom Stacking Dollies. First, a stack of enclosures on a Bottom Stacking Dolly is
rolled underneath the grid. The grid is lowered and the top box is attached to the grid. The Xvsg
and Xvsl chain rigging straps are attached at the front to achieve the desired vertical angles. The
four boxes are lifted high enough that another column of loudspeakers on a stacking dolly can be
rolled in under the suspended array. The array is then landed on top of the next stack of
loudspeakers and rigging hardware is attached between the flown stack and the stack on the
dolly. The entire column of loudspeakers is then lifted overhead. The process is repeated as
necessary to add more loudspeakers to the column. The process is identical for both the Bottom
Stacking Dolly and the Downfill Stacking Dolly.
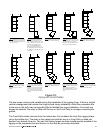
Figure 10 illustrates the technique used to construct a loudspeaker array with enclosures
transported on Front Dollies. The figure starts out showing four enclosures suspended overhead.
The array is lowered and a single enclosure on a front dolly is rolled into position behind the flown
array. The array is lowered until the bottom corner of the bottom box of the array lines up with the
rear corner of the box facing the ground on a Front Dolly. The Xvhl rear linking hinge is then
simultaneously installed in the rigging on the suspended box and the box on the dolly.
22