The Advanced MCACC menu
07
49
En
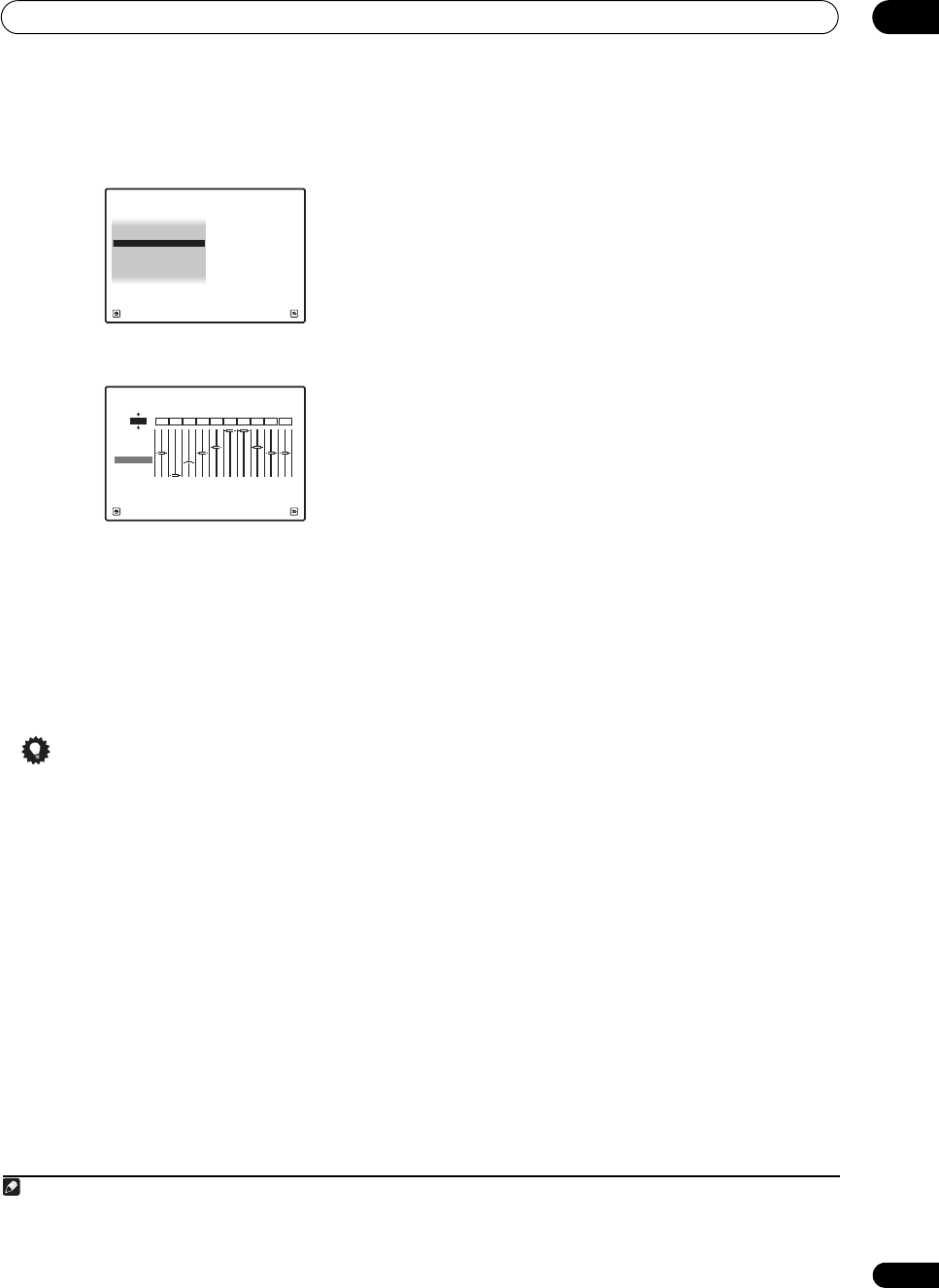
1 Select ‘
EQ Adjust
’ from the
Manual MCACC
setup
menu.
2 Select the channel(s) you want and adjust to your
liking.
Use / to select the channel.
Use / to select the frequency and / to boost or
cut the EQ. When you’re finished, go back to the top of
the screen and press to return to Ch, then use / to
select the channel.
•The OVER! indicator shows in the display if the
frequency adjustment is too drastic and might
distort. If this happens, bring the level down until
OVER! disappears from the display.
Tip
• Changing the frequency curve of one channel too
drastically will affect the overall balance. If the
speaker balance seems uneven, you can raise or
lower channel levels using test tones with the TRIM
feature. Use / to select TRIM, then use / to
raise or lower the channel level for the current
speaker.
3 When you’re finished, press
RETURN
.
You will return to the Manual MCACC setup menu.
Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
This setup minimizes the unwanted effects of room
reverberation by allowing you to calibrate your system
based on the direct sound coming from the speakers. It
can also provide you with a graphical output of the
frequency response of your room.
1
How to use Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
If you find that lower frequencies seem overly reverberant
in your listening room (i.e. it sounds ‘boomy’), or that
different channels seem to exhibit different reverb
characteristics, select EQ Pro. & S-Wave (or ALL) for the
Auto MCACC setting in Automatic MCACC (Expert) on
page 44 to calibrate the room automatically. This should
provide a balanced calibration that suits the
characteristics of your listening room.
If you still aren’t satisfied with the results, the manual
Advanced EQ Setup (below) provides a more
customized calibration of your system using the direct
sound of the speakers. This is done with the help of a
graphical output that can be displayed on-screen, or
using a computer (with software available from Pioneer
— see Connecting a PC for Advanced MCACC output on
page 72).
How to interpret the graphical output
The graph shows decibels on the vertical axis and time (in
milliseconds) on the horizontal axis. A straight line
indicates a flat-response room (no reverb), whereas a
sloping line indicates the presence of reverberation when
outputting test tones. The sloping line will eventually
flatten out when the reverberant sound stabilizes (this
usually takes about 100 ms or so).
By analyzing the graph, you should be able to see how
your room is responding to certain frequencies.
Differences in channel level and speaker distance are
taken into account automatically (compensation is
provided for comparison purposes), and the frequency
measurements can be examined both with and without
the equalization performed by this receiver.
2
Setting Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
according to your room characteristics
Using the manual setup, you can set the time period at
which the frequency response is analyzed, pinpointing
the time that is best for system calibration with your
particular room characteristics.
1. Fine Channel Level
2. Fine SP Distance
3. Standing Wave
1c.Manual MCACC
4. EQ Adjust
5. EQ Professional
A/V RECEIVER
Exit Return
63
[Hz]
125
[Hz]
250
[Hz]
500
[Hz]
1k
[Hz]
2k
[Hz]
4k
[Hz]
8k
[Hz]
16k
[Hz]
TRIM
dB
1c4.EQ Adjust
Exit Finish
0.0
Ch : L
-6.0-8.0 0.0 +8.5+3.0 +8.5 0.0 0.0+3.0
A/V RECEIVER
MCACC
M1.MEMORY1
Note
1 This system allows you to customize your system calibration with the help of a graphical output that can be displayed on-screen, or using a
computer (with software available from Pioneer—see Connecting a PC for Advanced MCACC output on page 72 for more on this).
2 Note that due to an effect known as ‘group delay’, lower frequencies will take longer to be generated than higher frequencies (this is most
obvious when comparing the frequencies at 0 ms). This initial slope is not a problem (i.e. excessive reverb) with your listening room.
SC07-05.book Page 49 Friday, April 25, 2008 11:59 AM
