27
Examples of Use
Examples of Use
This section shows some examples of how you can use the MMP-2.
* Before hooking up or turning on any equipment, make sure the volume on all devices is turned down.
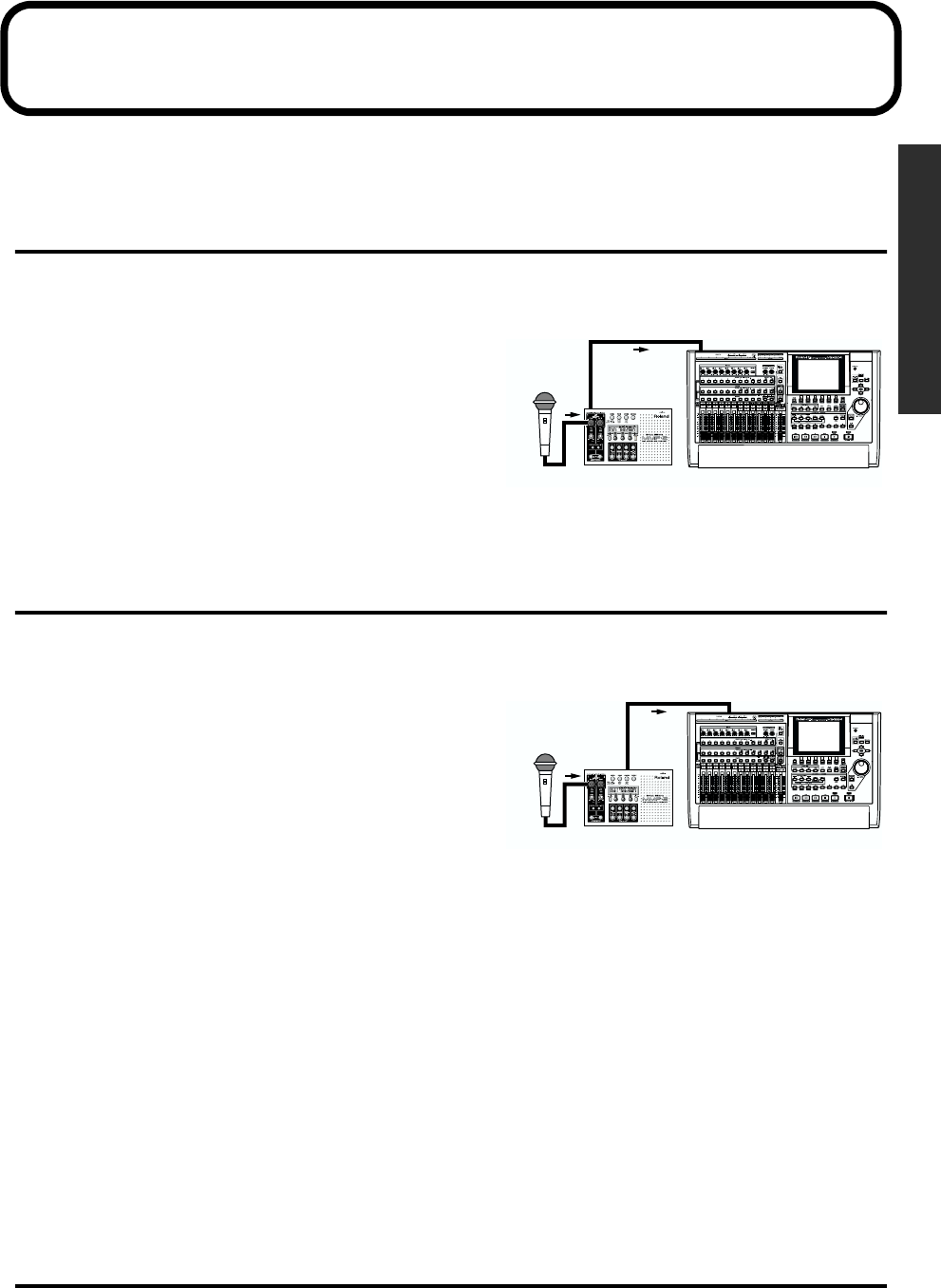
Analog Input to Analog Output
The microphone input is output from the MMP-2 as an analog signal and sent to a recording device or a
mixer.
fig.e.mic-MMP2-a-VS1824.eps
1. Connect the microphone to [MIC IN].
2. Connect the destination device to [LINE OUT].
3. Use the [PHANTOM/PHASE/LO-CUT] buttons and
other controls to set the phantom power setting so it
matches the type of microphone (p. 17).
4. Use the [METER] button to display the input meter.
5. Refer to the meters and the [PEAK] indicator and adjust the [PAD] and [SENS] settings.
Analog Input to Digital Output
The microphone input is output from the MMP-2 as an S/PDIF-standard digital signal and sent to a
recording device or the like. (The AES/EBU-standard jacks can also be used in the same way.)
fig.e.mic-MMP2-SPDIF-VS1824.eps
1. Connect the microphone to [MIC IN].
2. Connect the destination device to [DIGITAL OUT].
3. Use the [PHANTOM/PHASE/LO-CUT] buttons and
other controls to set the phantom power setting so it
matches the type of microphone (p. 17).
4. Use the [METER] button to display the input meter.
5. Refer to the meters and the [PEAK] indicator and adjust the [PAD] and [SENS] settings.
6. Use the [SYSTEM] button and other controls to set “CLOCK” to “INT,” to set “FREQ” to an appropriate
value for the destination device, and to set “AUDIO” to “MIC” (p. 26).
7. Make the clock setting on the destination device.
microphone
MMP-2
recorder
microphone
MMP-2
recorder


















