51
Typical examples of piping
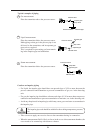
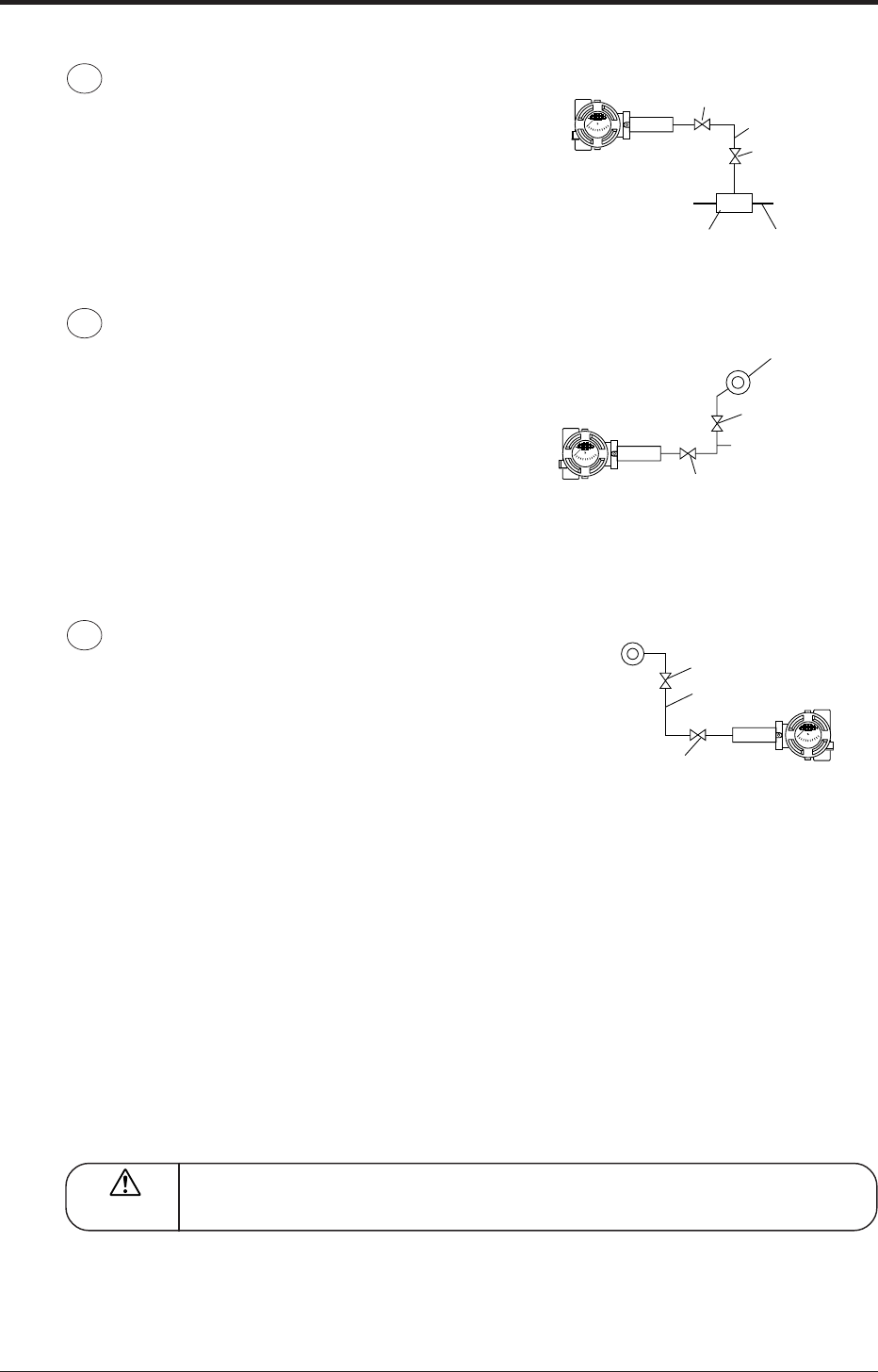
Gas measurement
Place the transmitter above the pressure source.
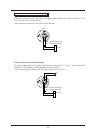
Liquid measurement
Place the transmitter below the pressure source.
Make piping so that gas in the process pipe is not
delivered to the transmitter, and incorporate gas
reservoirs as required.
This is required for preventing gas from remain-
ing in the impulse pipe and transmitter.
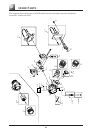
Steam measurement
Place the transmitter below the pressure source.
Impulse pipe
Stop valve
Process pipe
Pressure source
Manual valve
0
20
40
60
80
100
Impulse pipe
Manual valve
Process pipe
Stop valve
0
20
40
60
80
100
Pressure source
Cautions on impulse piping
• For liquid, the impulse pipe should have an upward slope of 1/10 or more between the
process connection and transmitter to prevent accumulation of gas, etc. in the detecting
unit.
• For gas, the impulse pipe should have a downward slope of 1/10 or more between process
connection and transmitter to prevent accumulation of moisture, etc. in the detecting unit.
•Avoid any sharp bends in impulse pipe which may cause gas or moisture to accumulate in
the impulse pipe.
Impulse pipe
Manual valve
Pressure source
Stop valve
0
20
40
60
80
100
CAUTION
The impulse pipe used should be suitable for the working temperature, pressure,
etc.
1
2
3
• Take care not to apply an excessive force to the transmitter during its connection.
•When the measurement fluid is likely to freeze in the cover of measurement chamber, the
cover needs to be warmed up with steam or a heater.