Reference Manual
00809-0100-4697, Rev EA
October 2011
C-3
Rosemount 848T
DEVICE DESCRIPTIONS Device Descriptions (DD) are specified tool definitions that are associated
with the Resource and Transducer Blocks. Device descriptions provide the
definition and description of the function blocks and their parameters.
To promote consistency of definition and understanding, descriptive
information, such as data type and length, is maintained in the device
description. Device Descriptions are written using an open language called
the Device Description Language (DDL). Parameter transfers between
function blocks can be easily verified because all parameters are described
using the same language. Once written, the device description can be stored
on an external medium, such as a CD-ROM or diskette. Users can then read
the device description from the external medium. The use of an open
language in the device description permits interoperability of function blocks
within devices from various vendors. Additionally, human interface devices,
such as operator consoles and computers, do not have to be programmed
specifically for each type of device on the bus. Instead their displays and
interactions with devices are driven from the device descriptions.
Device descriptions may also include a set of processing routines called
methods. Methods provide a procedure for accessing and manipulating
parameters within a device.
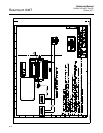
BLOCK OPERATION In addition to function blocks, fieldbus devices contain two other block types
to support the function blocks. These are the resource block and the
transducer block.
Instrument- Specific
Function Blocks
Resource Blocks
Resource blocks contain the hardware–specific characteristics associated
with a device; they have no input or output parameters. The algorithm within a
resource block monitors and controls the general operation of the physical
device hardware. The execution of this algorithm is dependent on the
characteristics of the physical device, as defined by the manufacturer. As a
result, the algorithm may cause the generation of events. There is only one
resource block defined for a device. For example, when the mode of a
resource block is “Out of Service (OOS),” it impacts all of the other blocks.
Transducer Blocks
Transducer blocks connect function blocks to local input/output functions.
They read sensor hardware and write to effector (actuator) hardware. This
permits the transducer block to execute as frequently as necessary to obtain
good data from sensors and ensure proper writes to the actuator without
burdening the function blocks that use the data. The transducer block also
isolates the function block from the vendor–specific characteristics of the
physical I/O.
Alerts When an alert occurs, execution control sends an event notification and waits
a specified period of time for an acknowledgment to be received. This occurs
even if the condition that caused the alert no longer exists. If the
acknowledgment is not received within the pre-specified time-out period, the
event notification is retransmitted, assuring that alert messages are not lost.