Adjustable parameters
The network function enables adjustment of
the following parameters. Make adjustments
in line with the reproduced frequency band
and characteristics of each connected speaker
unit.
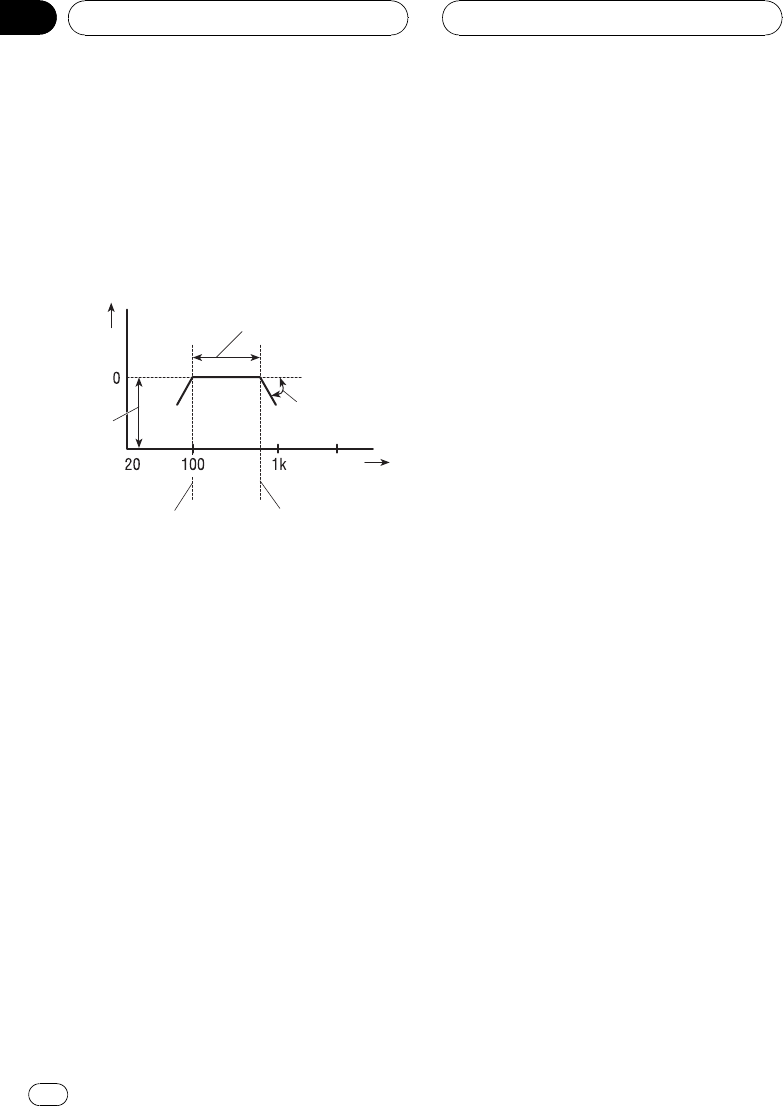
Reproduced frequency band
Pass
Slope (dB/oct.)
Frequency
(Hz)
Level
Level
(dB)
Cut-off frequency
of LPF
Cut-off frequency
of HPF
Reproduced frequency band
Adjusting the HPF (high-pass filter) or LPF
(low-pass filter) cut-off frequency lets you set
the reproduced frequency band for each
speaker unit.
! The HPF cuts frequencies (low) below the
set frequency, letting high frequencies
through.
! The LPF cuts frequencies (high) above the
set frequency, letting low frequencies
through.
Level
The difference in reproduced levels between
speaker units can be corrected.
Slope
Adjusting the HPF/LPF slope (filter attenuation
slope) lets you adjust the continuity of sound
between speaker units.
! The slope indicates the number of decibels
(dB) the signal is attenuated when the fre-
quency is one octave higher (lower) (Unit:
dB/oct.). The steeper the slope, the more
the signal is attenuated.
Phase
You can switch phase (normal, reverse) for
each speaker units input signal. When the
continuity of sound between speakers is im-
precise, try switching phase. This may improve
the continuity of sound between speakers.
Points concerning network
adjustments
Cut-off frequency adjustment
! With the low-range speaker installed in the
rear tray, if you set Low LPF cut-off fre-
quency high, bass sound is separated so
that it appears to come from the rear. You
are recommended to set Low LPF cut-off
frequency to 100 Hz or lower.
! The maximum input power setting for mid-
dle- and high-range speakers is usually
lower than that for low-range speakers. Re-
member that if Mid HPF or High HPF cut-
off frequency is set lower than required,
strong bass signal input may damage the
speaker.
Level adjustment
The basic frequencies of many musical instru-
ments are in the middle range. First perform
middle-range level adjustment, followed by
high-range and then low-range level adjust-
ment in that order.
Slope adjustment
! If you set a small absolute value for the
slope (for a gentle slope), interference be-
tween adjacent speaker units can easily re-
sult in degraded frequency response.
! If you set a large absolute value for the
slope (for a steep slope), continuity of
sound between speaker units is degraded,
and sounds appear to be separated.
Audio Adjustments
En
42
Section
08


















