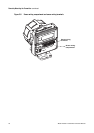
Model IFT9701 Transmitter Instruction Manual 23
Power Supply and Output Wiring continued
Getting Started Power Supply and Output WiringMounting the Remote TransmitterBefore You Begin
4.4.2 Milliamp output connected to Bell 202 multidrop network
Devices in a Bell 202 multidrop network communicate by sending and receiving signals to and from
one another. HART protocol supports up to 15 transmitters in a Bell 202 multidrop network.
Other Rosemount SMART FAMILY transmitters can also participate in a HART-compatible network.
• A Bell 202 multidrop network uses twisted-pair wire, and allows only digital communication.
• A HART Communicator or other HART-compatible control system can communicate with
any device in the network over the same 2-wire pair.
Using multiple transmitters in a HART-compatible network requires assigning a unique address other
than 0 to each transmitter. Assigning an address other than 0 to the transmitter causes the primary mA
output to remain at a constant 4 mA level.
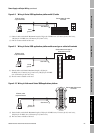
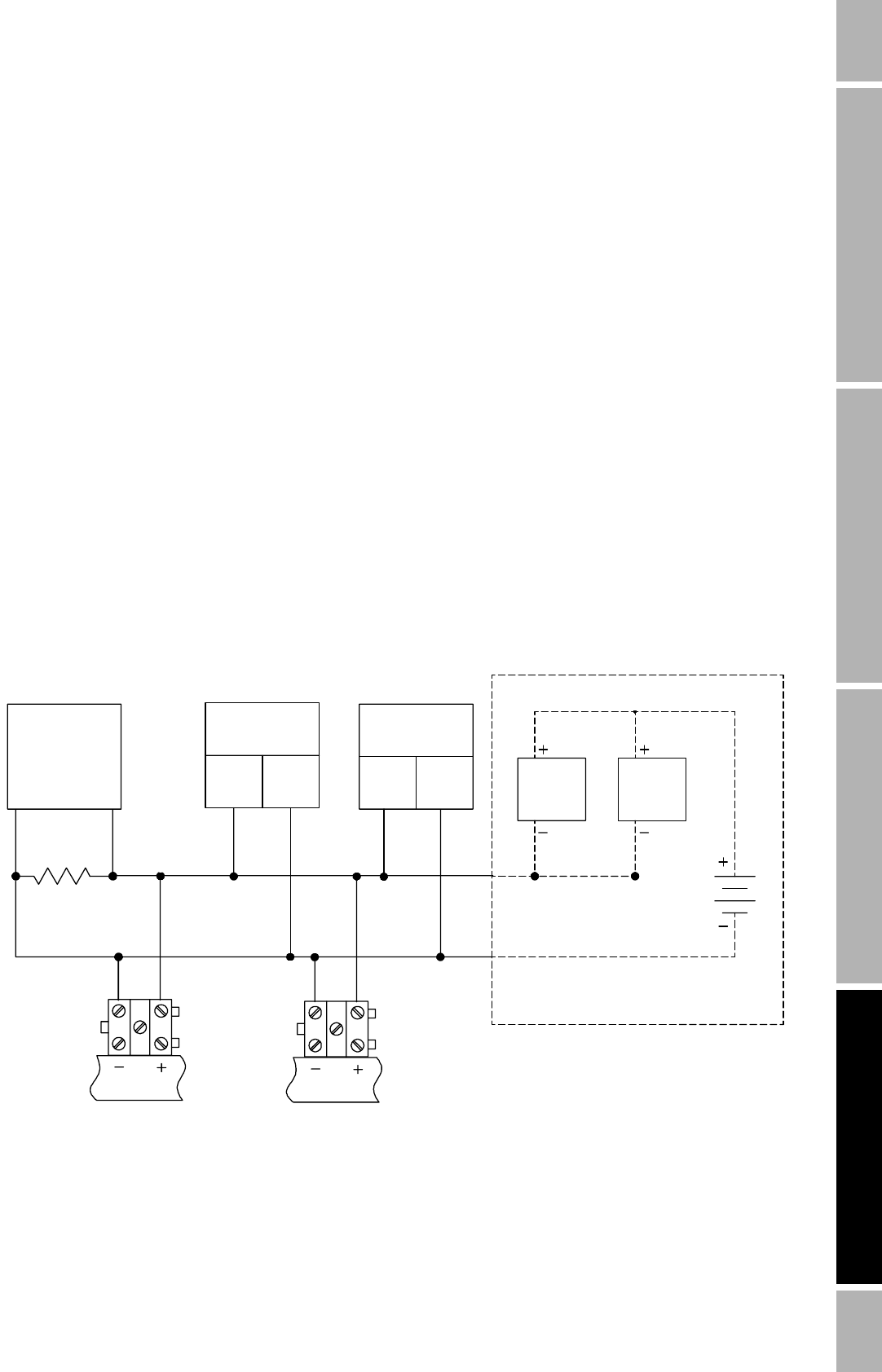
Figure 4-4 shows how to connect wiring for a HART-compatible network.
• The maximum number depends upon the type of transmitters, the method of installation, and
other external factors.
• The primary mA output must produce a 4–20 mA current for the Bell 202 physical layer. The
Bell 202 layer will work when the primary mA output is at or above 2 mA output.
• SMART FAMILY devices require a minimum loop resistance of 250 ohms. Loop resistance
must not exceed 600 ohms.
Connect the mA outputs from each transmitter together so they terminate at a common load resistor,
with at least 250 ohms impedance, installed in series.
Figure 4-4 Typical HART network wiring
Note: For optimum HART communication, make
sure the output loop is single-point-grounded to
an instrument grade ground.
HART comm
tool
RFT9739
field-mount
RFT9739
rack-mount
SMART
FAMILY
device
SMART
FAMILY
device
DC source required for
other HART 4–20mA
passive transmitters
250 ohm
load
PV+
17
PV−
18
PV+
CN2−
Z30
PV−
CN2−
D30
4–20 mA
IFT9701
IFT9701
4–20 mA
24
DC