Using WT3 to Design a Zobel Network
Zobel networks are used to control the impedance of a loudspeaker driver in the upper frequency range
where voice coil inductance normally causes the impedance to rise with increasing frequency. Zobel
networks are used to help crossovers do a better job of keeping the highs from passing to the woofer.
A Zobel consists of a resistor and capacitor connected in series and attached between the terminals of
the driver. The resistor is normally selected to match the nominal impedance of the system. The
capacitor value can then be calculated or, in this case, determined empirically. Because WT3 is able to
perform impedance sweeps in just a few seconds it can be used for any type of repetitive adjust and
measure process...such as designing a Zobel network to neutralize the inductance of a driver. Yes, you
can calculate the component values for a Zobel network but sometimes it is easier to just clip a
resistor/capacitor network across the driver and see what you get for the impedance.
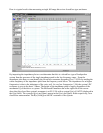
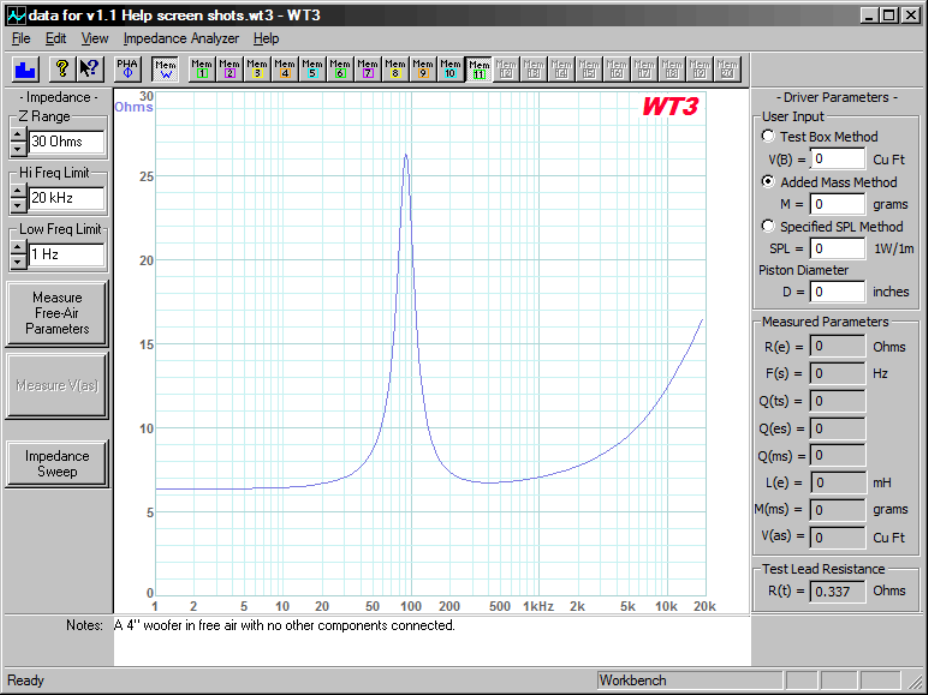
Below is the impedance response of a small woofer with no other components connected. Notice the
rising impedance above 500 Hz. We would like to design a Zobel network to compensate the woofer
and restore the impedance to some nominal value above 500 Hz.
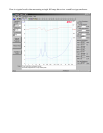
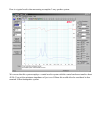
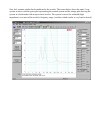
With a DC resistance of 5.5 Ohms this would most likely be considered to be an 8 Ohm driver. So let's
set the resistor value to about 8 Ohms. Looking in my parts bin I see the closest values on hand are 5
and 10 Ohms. Let's use 10 Ohms so that we tend to under compensate. We'll select the capacitor value
by starting too low and stepping up the capacitor until the impedance response looks about as flat as