48
RQT6894
Reference
Language code list
Abkhazian: 6566
Afar: 6565
Afrikaans: 6570
Albanian: 8381
Ameharic: 6577
Arabic: 6582
Armenian: 7289
Assamese: 6583
Aymara: 6588
Azerbaijani: 6590
Bashkir: 6665
Basque: 6985
Bengali; Bangla
: 6678
Bhutani: 6890
Bihari: 6672
Breton: 6682
Bulgarian: 6671
Burmese: 7789
Byelorussian: 6669
Cambodian: 7577
Catalan: 6765
Chinese: 9072
Corsican: 6779
Croatian: 7282
Czech: 6783
Danish: 6865
Dutch: 7876
English: 6978
Esperanto: 6979
Estonian: 6984
Faroese: 7079
Fiji: 7074
Finnish: 7073
French: 7082
Frisian: 7089
Galician: 7176
Georgian: 7565
German: 6869
Greek: 6976
Greenlandic: 7576
Guarani: 7178
Gujarati: 7185
Hausa: 7265
Hebrew: 7387
Hindi: 7273
Hungarian: 7285
Icelandic: 7383
Indonesian: 7378
Interlingua: 7365
Irish: 7165
Italian: 7384
Japanese: 7465
Javanese: 7487
Kannada: 7578
Kashmiri: 7583
Kazakh: 7575
Kirghiz: 7589
Korean: 7579
Kurdish: 7585
Laotian: 7679
Latin: 7665
Latvian, Lettish
: 7686
Lingala: 7678
Lithuanian: 7684
Macedonian: 7775
Malagasy: 7771
Malay: 7783
Malayalam: 7776
Maltese: 7784
Maori: 7773
Marathi: 7782
Moldavian: 7779
Mongolian: 7778
Nauru: 7865
Nepali: 7869
Norwegian: 7879
Oriya: 7982
Pashto, Pushto
: 8083
Persian: 7065
Polish: 8076
Portuguese: 8084
Punjabi: 8065
Quechua: 8185
Rhaeto-Romance
: 8277
Telugu: 8469
Thai: 8472
Tibetan: 6679
Tigrinya: 8473
Tonga: 8479
Turkish: 8482
Turkmen: 8475
Twi: 8487
Ukrainian: 8575
Urdu: 8582
Uzbek: 8590
Vietnamese: 8673
Volapük: 8679
Welsh: 6789
Wolof: 8779
Xhosa: 8872
Yiddish: 7473
Yoruba: 8979
Zulu: 9085
Romanian: 8279
Russian: 8285
Samoan: 8377
Sanskrit: 8365
Scots Gaelic: 7168
Serbian: 8382
Serbo-Croatian
: 8372
Shona: 8378
Sindhi: 8368
Singhalese: 8373
Slovak: 8375
Slovenian: 8376
Somali: 8379
Spanish: 6983
Sundanese: 8385
Swahili: 8387
Swedish: 8386
Tagalog: 8476
Tajik: 8471
Tamil: 8465
Tatar: 8484
Glossary
WMA/MP3/JPEG information
pDiscs must conform to ISO9660 level 1 or 2 (except for extended formats).
pThis unit is compatible with multi-session but if there are a lot of sessions it
takes more time for play to start. Keep the number of sessions to a mini-
mum to avoid this.
[WMA]
pNoise may occur when playing WMA files.
pYou cannot play WMA files that are copy protected.
pWMA files must have the extension “.WMA” or “.wma”.
[MP3]
pThis unit is not compatible with ID3 tags.
pIf you play an MP3 track that includes still picture data, it will take some
time before the music itself starts playing and the elapsed time will not be
displayed during this time. Even after the track starts, the correct play time
will not be displayed.
pMP3 files must have the extension “.MP3” or “.mp3”.
[JPEG]
To view JPEG files on this unit:
—Take them on a digital camera that meets the DCF (Design rule for
Camera File system) standard. Some digital cameras have functions that
are not supported by the DCF standard like automatic picture rotation
which may render a picture un-viewable.
—Do not alter the files in any way or save them under a different name.
—Ensure they have the extension “.JPG” or “.jpg”, “.JPEG” or “.jpeg”.
p
This unit cannot display moving pictures, MOTION JPEG and other such
formats, still pictures other than JPEG (i.e. TIFF) or play associated sound.
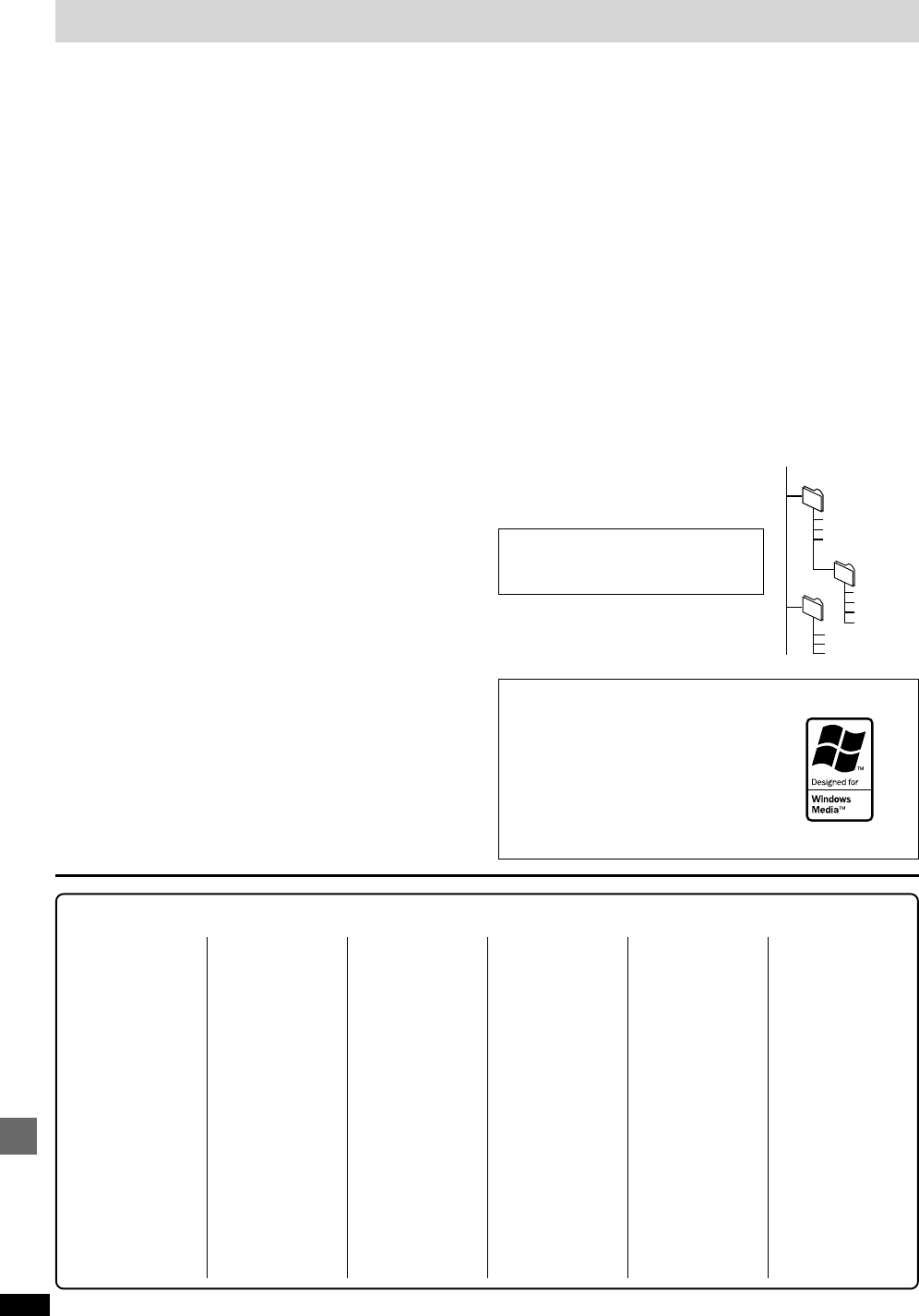
Naming folders and files
At the time of recording, give folders and file
names 3-digit prefixes in the order you want to
play them (this may not work at times).
Decoder
A decoder restores the coded audio signals on DVDs to normal. This is
called decoding.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals developed by Dolby Laboratories.
Apart from stereo (2-channel) audio, these signals can also be multi-
channel audio. A large amount of audio information can be recorded on one
disc using this method.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie theaters around the world.
There is good separation between the channels, so realistic sound effects
are possible.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the lowest level of sound that can
be heard above the noise of the equipment and the highest level of sound
before distortion occurs.
Frame still and field still
Frames are the still pictures that go together to make a moving picture.
There are about 30 frames shown each second.
One frame is made up of two fields. A regular television shows these fields
one after the other to create frames.
A still is shown when you pause a moving picture. A frame still is made up of
two alternating fields, so the picture may appear blurred, but overall quality
is high.
A field still is not blurred, but it has only half the information of a frame still so
picture quality is lower.
I/P/B
MPEG 2, the video compression standard adopted for use with DVD-Video,
codes frames using these 3 picture types.
I: Intra coded picture (I-picture)
This picture has the best quality and is the best to use when adjusting
the picture.
P: Predictive coded picture (P-picture)
This picture is calculated based on past I or P-pictures.
B: Bidirectionally-predictive coded picture (B-picture)
This picture is calculated by comparing past and future I and
P-pictures so it has the lowest volume of information.
Linear PCM (pulse code modulation)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar to those found on CDs.
Playback control (PBC)
If a Video CD has playback control, you can select scenes and information
with menus.
MPEG Layer-3 audio decoding technology
licensed from Fraunhofer IIS and Thomson
multimedia.
001
root
001group
004track.mp3
005track.mp3
006track.mp3
002group
003group 007track.mp3
008track.mp3
009track.mp3
010track.mp3
011track.mp3
012track.mp3
013track.mp3
Windows Media, and the Windows logo are
trademarks, or registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries.
WMA is a compression format developed
by Microsoft Corporation. It achieves the
same sound quality as MP3 with a file size
that is smaller than that of MP3.
e.g. [MP3]