24
Troubleshooting
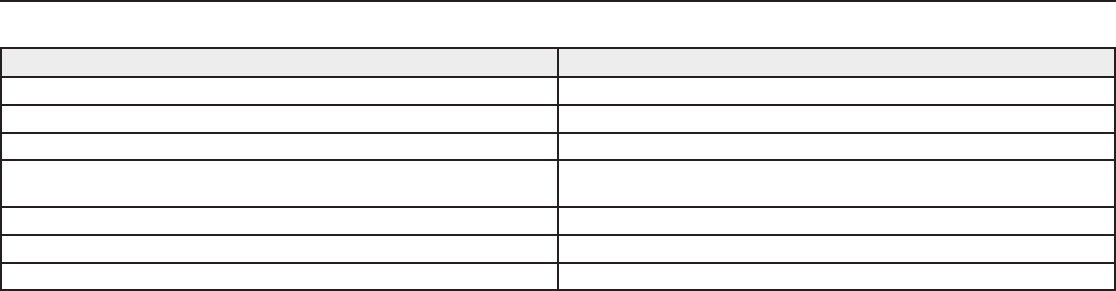
Issue See Solution...
No Sound Power, Cables, Radio Frequency, or Encryption Mismatch
Faint sound or distortion Gain
Lack of range, unwanted noise bursts, or dropouts RF
Cannot turn transmitter off or change frequency settings, or can't program
receiver
Interface locks
Encryption Mismatch message Encryption Mismatch
Firmware Mismatch message Firmware Mismatch
Antenna Fault message RF
Power
Make sure that the receiver and transmitter are receiving sufficient voltage.
Check the battery indicators and replace the transmitter batteries if
necessary.
Gain
Adjust the system gain on the front of the receiver. Ensure the output level
(XLR output only) on the back of the receiver corresponds to the input of the
mixing console, amplifier, or DSP.
Cables
Check that all cables and connectors are working correctly.
Interface Locks
The transmitter and the receiver can be locked to prevent accidental or
unauthorized changes. A locked feature or button will produce the Locked
screen on the LCD panel.
Encryption Mismatch
Re-sync all receivers and transmitters after enabling or disabling encryption.
Firmware Mismatch
Paired transmitters and receivers must have the same firmware version
installed to ensure consistent operation. See Firmware topic for firmware
update procedure.
Radio Frequency (RF)
RF LEDs
If neither blue RF Diversity LED is illuminated, then the receiver is not
detecting the presence of a transmitter.
The amber
RF Signal Strength LEDs indicate the amount of RF power being
received. This signal could be from the transmitter, or it could be from an
interfering source, such as a television broadcast. If more than one or
two of the amber RF LEDs are still illuminated while the transmitter is off,
then that channel has too much interference, and you should try a different
channel.
The red
RF LED indicates RF overload. This will usually not cause a
problem unless you are using more than one system at the same time, in
which case, it can cause interference in the other system.
Compatibility
• Perform a Scan and Sync to ensure the transmitter and receiver are set
to the same group and channel.
• Look at the label on the transmitter and receiver to make sure they are in
the same band (G50, J50, L50, etc...).
Reducing Interference
• Perform a group or channel scan to find the best open frequency.
Perform a sync to transfer the setting to the transmitter.
• For multiple systems, check that all systems are set to channels in the
same group (systems in different bands do not need to be set to the
same group).
• Maintain a line of sight between transmitter and receiver antennas.
• Move receiver antennas away from metal objects or other sources of
RF interference (such as CD players, computers, digital effects, network
switches, network cables and Personal Stereo Monitor (PSM) wireless
systems).
• Eliminate RF overload (see below).
Increasing Range
If the transmitter is more than 6 to 60 m (20 to 200 ft) from the receiver
antenna, you may be able to increase range by doing one of the following:
• Reduce interference (see above).
• Increase transmitter RF power level.
• Use Normal mode instead of High Density mode.
• Use an active directional antenna, antenna distribution system, or other
antenna accessory to increase RF range.
Eliminating RF Overload
If you see the red RF LED on a receiver, try the following:
• Reduce the transmitter RF power level
• Move the transmitter further away from the receiver—at least 6 m (20 ft)
• If you are using active antennas, reduce antenna or amplifier gain.
• Use omnidirectional antennas
Antenna Faults
The Antenna Fault message indicates a short circuit condition at an antenna
port.
• Check antennas and cables for damage
• Ensure that antenna ports are not overloaded
• Check antenna bias voltage setting. Turn off voltage if using passive
antennas.