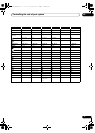
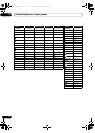
The Advanced MCACC menu
10
77
En
it results in an overly resonant (‘boomy’) sound. The
Standing Wave Control uses filters to reduce the effect of
overly resonant sounds in your listening area. During
playback of a source, you can customize the filters used
for Standing Wave Control for each of your MCACC
presets.
1
1 Select ‘
Standing Wave
’ from the
Manual MCACC
setup menu.
2 Adjust the parameters for the Standing Wave
Control.
• Filter Channel – Select the channel to which you will
apply the filter(s): MAIN (all except center channel
and subwoofer), Center or SW (subwoofer).
• TRIM (only available when the filter channel above is
SW) – Adjust the subwoofer channel level (to
compensate for the difference in output p ost-filter).
• Freq / Q / ATT – These are the filter parameters where
Freq represents the frequency you will be targeting
and Q is the bandwidth (the higher the Q, the
narrower the bandwidth, or range) of the attenuation
(ATT, the amount of reduction to the targeted
frequency).
3 When you’re finished, press
RETURN
.
You will return to the Manual MCACC setup menu.
Acoustic Calibration EQ Adjust
• Default setting: ON/0.0dB (all channels/bands)
Acoustic Calibration Equalization is a kind of room
equalizer for your speakers (excluding the subwoofer). It
works by measuring the acoustic characteristics of your
room and neutralizing the ambient characteristics that
can color the original sour ce material (providing a ‘flat’
equalization setting). If you’re not satisfied with the
adjustment provided in Automatically conducting
optimum sound tuning (Auto MCACC) on page 37 or
Automatic MCACC (Expert) on page 73, you can also
adjust these settings manually to get a frequency
balance that suits your tastes.
1 Select ‘
EQ Adjust
’ from the
Manual MCACC
setup
menu.
2 Select the channel(s) you want and adjust to your
liking.
Use / to select the channel.
Use / to select the frequency and / to boost or
cut the EQ. When you’re finished, go back to the top of
the screen and press to return to Ch, then use / to
select the channel.
•The OVER! indicator shows in the display if the
frequency adjustment is too drastic and might
distort. If this happens, bring the level down until
OVER! disappears from the display.
Tip
•Changing the frequency curve of one channel too
drastically will affect the overall balance. If the speaker
balance seems uneven, you can raise or lower channel
levels using test tones with the
TRIM
feature. Use
/
to select
TRIM
, then use
/
to raise or lower the
channel level for the current speaker.
3 When you’re finished, press
RETURN
.
You will return to the Manual MCACC setup menu.
Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
This setup minimizes the unwanted effects of room
reverberation by allowing you to calibrate your system
based on the direct sound coming from the speakers.
How to use Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
If you find that lower frequencies seem overly reverberant
in your listening room (i.e. it sounds ‘boomy’), or that
different channels seem to exhibit different reverb
characteristics (when Type A or Type B shown on the
diagrams on the following applies), select EQ Pro. & S-
Wave (or ALL) for the Auto MCACC setting in Automatic
MCACC (Expert) on page 73 to calibrate the room
automatically.
• Type A: Reverberance of high vs. low frequencies
• Type B: Reverb characteristics for different
channels
If the pattern is as shown above, select the 30-50ms
setting. If not, this setting is not necessary.
Note
1 Standing Wave control filter settings cannot be changed during playback of sources using the HDMI connection.
Level
Low
frequencies
Acoustic Cal. EQ Pro.
calibration range
Time
(in msec)
80 160
High
frequencies
Conventional MCACC
EQ calibration range
0
Level
Front L
Acoustic Cal. EQ Pro.
calibration range
Time
(in msec)
80 160
Front R
Conventional MCACC
EQ calibration range
0
VSX-1325_UXJCB.book 77 ページ 2010年3月9日 火曜日 午後3時4分