4 DSP
32 CONTENTS TS-590S
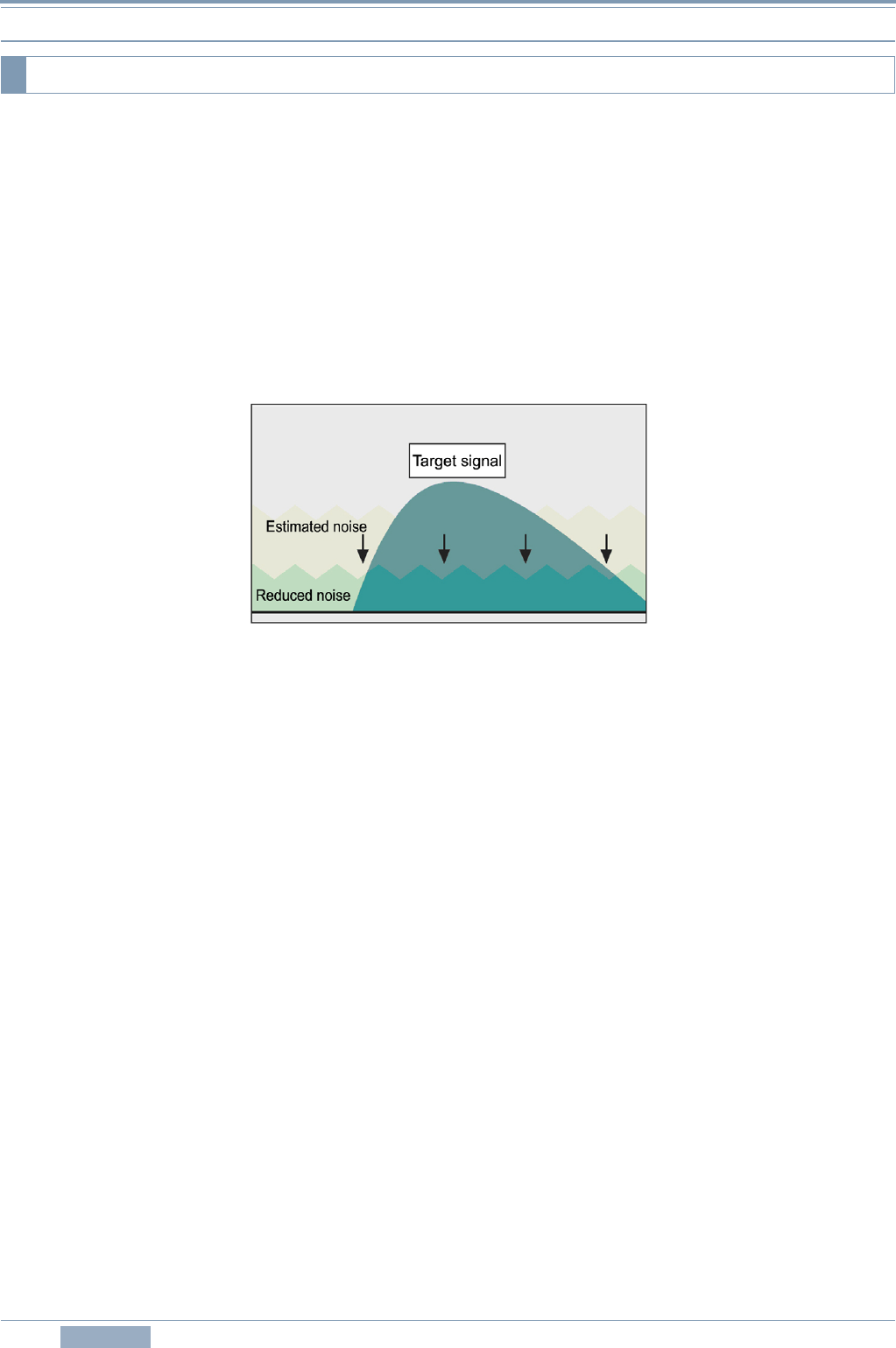
Unlike the conventional noise reduction methods, the spectral subtraction method of NR1 is a brand
new approach of noise reduction developed for the TS-590S. NR1 estimates the noise component
and takes away (subtracts) the estimated noise component from the RX signal to make the target
signal emerge (Figure 4-13).
This method was developed with a focus on improving the intelligibility of a weak SSB signal.
Compared with conventional NR1 (based on a line enhancer), audio output with minimized
degradation of audio quality, while higher-pitched components are affected less, is obtained while
noise is effectively reduced. In developing NR1 based on spectral subtraction, a new technology has
been invented to reduce the introduction of musical noise (tonal “blip blip” sound) that is inherently
generated by spectral subtraction. Hence, the production of musical noise in the spectral subtraction
has been substantially suppressed.
Figure 4-13 Conceptual Scheme of NR1 Based on Spectral Subtraction
The new spectral subtraction-based NR1 allows selection of the NR effect level more smoothly than
the conventional NR1 method. Use the effect level of your choice according to the receive
conditions.
Note, however, since the noise estimation process of the spectral subtraction NR1 identifies any
steady sound as a noise component, beat interference or a CW signal is also judged as a target of
noise reduction. Meanwhile, the conventional noise reduction (based on a line enhancer) functions
to emphasize beat interference or a CW signal. Because the new spectral subtraction-based NR1 is
not intended for elimination of a CW signal or beat interference, you cannot expect a noticeable effect
against those signals. To remove beat interference or a CW signal, use beat cancel (BC) instead.
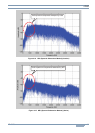
Below you can see the result of frequency analysis conducted on the receive audio containing an
audio signal while NR1 is inactive in Figure 4-14 and the result while NR1 is active in Figure 4-15.
4.6.4 NR1 (Spectral Subtraction Method) (AF Processing)