D13841.08
10.2007
32
Table of
Contents
Trademarks &
Copyright
Patents &
Disclaimers
Safety/
Environmental
To Get You
Up and Going
Using the 3G
Gateway
Viewing the
System Status
Configuring
the 3G Gateway
Maintenance
& Upgrade
Services
Dial Plan
Examples
Contact
Information
TANDBERG 3G Gateway
USER GUIDE
Configuring
the 3G Gateway
TANDBERG 3G GATEWAY
USER GUIDE
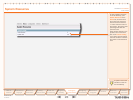
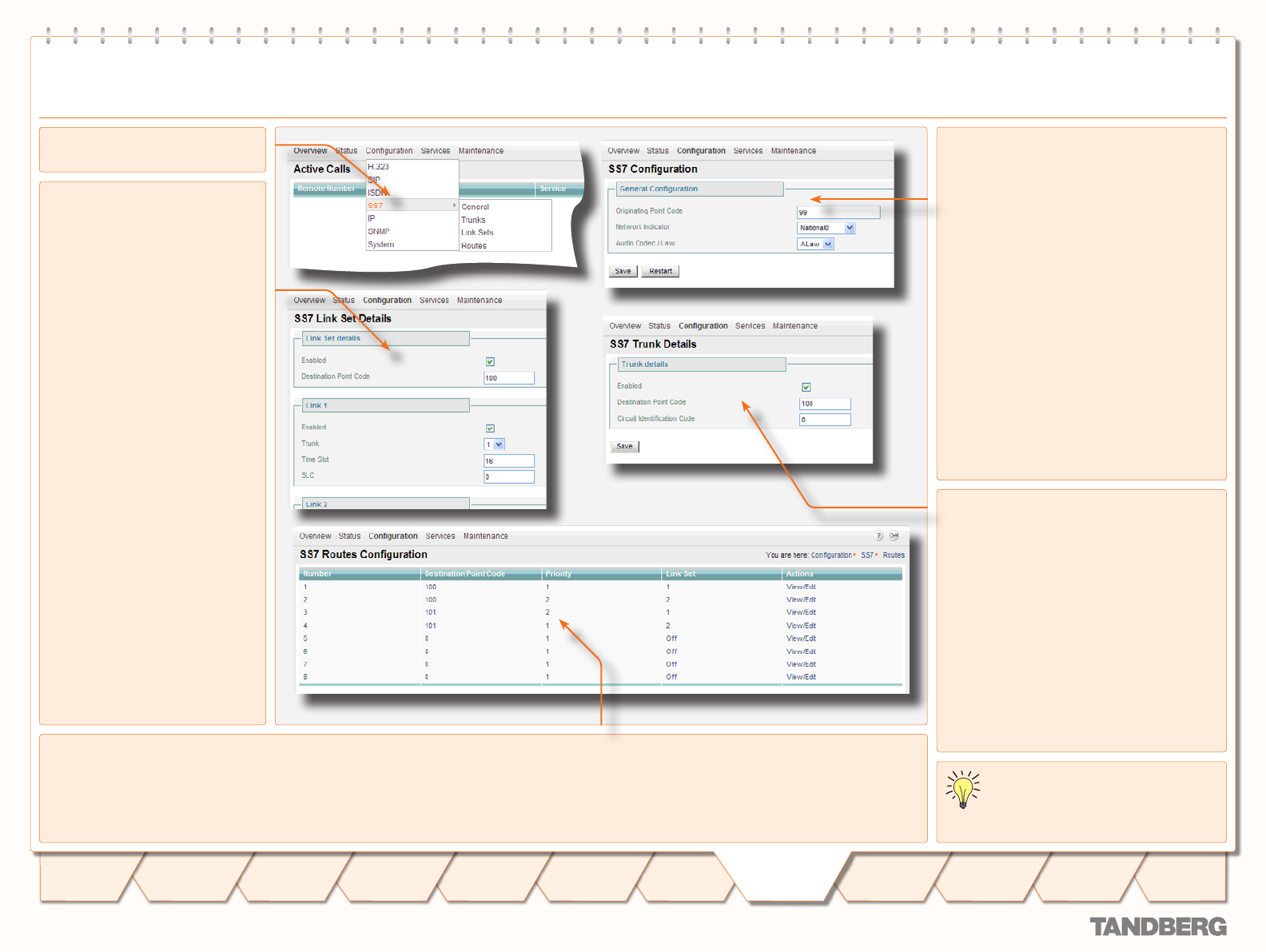
Select SS7 to access the SS7
Configuration
pane.
General
Originating Point Code (OPC)
• . A number in
the range 0–2
14
, which uniquely identifies a
signalling point, in this case the 3G Gateway,
within a telephone network. This number
consists of three parts, viz. a network,
cluster and member number, and will be
provided by the network operator.
Network indicator• . A two bit data field
within the Service Information Octet of
the Message Signal Unit that permits
discrimination between national and
international messages.
Audio Codec / Law• . Either ALAW or ULAW. An
a-law algorithm is a standard companding, i.e.
compressing and expanding, algorithm, used
in European digital communication systems
to optimize, i.e. modify, the dynamic range
of an analogue signal for digitizing. The µ-law
algorithm is similar to a-law and used in North
American and Japanese systems.
SS7 Conguration
Trunks
A maximum of four PRIs or SS7 trunks, i.e.
cables carrying E1/T1, can be enabled in the 3G
Gateway.
Mode• . Enable or disable a trunk.
Destination Point Code (DPC)• . Uniquely
identifies the destination signalling point of
the trunk. It will be provided by the network
operator.
CIC• . The Circuit Identification Code is a
unique identifier for a data time slot in
a cable (trunk). In this case the CIC acts
as base address and can be defined for
each SS7 trunk and sets the first time-slot
number of the respective SS7 trunk.
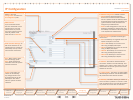
Link Set Details
A link is a time slot within a trunk
used for signalling. Link sets are
typically used for signalling fail-over
purposes to one switch.
Enabled• . Checking this box ena-
bles at least one signalling link in
a link set.
Destination Point Code• . Uniquely
identifies the destination signal-
ling point of the link. This can dif-
fer from the DPC of the trunk, e.g.
the DPC of a Signalling Transfer
Point (STP), see example 2 on the
following pages.
Enabled• . Link1 is checked by
default. Whereas, a second link
box can be checked to define
an extra signalling link for fail-
over purposes.
Trunk• . Number of the trunk
(1–4) in which a time slot is
reserved for signalling.
Time slot• . Number of the time
slot, within aforementioned
trunk, reserved for signalling.
SLC• .A Signalling Link Code is a
unique link number provided by
the network operator to identify
a link.
To provide a better understanding
of the settings discussed here, two
examples are given on the following
pages.
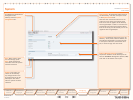
Routes
Routes are typically used for signalling fail-over
purposes via multiple switches.
Destination Point Code.• Unique identifier
indicating the destination signalling point of
a trunk.
Priority.• Priority level of the route to the
destination signalling point. Fail-over signalling
paths will be followed according to this priority.
Link set.• Indicates the link to the destination
signalling point according to the above
mentioned priority setting. When set to off
the respective route is disabled.