Reference Manual
00809-0100-4514, Rev BA
January 2008
3-7
Rosemount 1154
1. Calibrate the unit per preceding section to output = 4 mA at –100
inH
2
O and 20 mA at 300 inH
2
O.
2. Calculate correction factor:
3. Calculate zero adjustment correction in terms of pressure:
4. Convert pressure correction to percent of input span:
5. Calculate correction in terms of output span (mA):
6. Add the milliamp correction to the ideal zero output (4 mA). This is the
corrected ideal zero output:
7. Calculate full-scale adjustment correction in terms of pressure:
8. Repeat step 4 with the results of step 7:
9. Repeat step 5 with the result of step 8:
10. Add the mA correction to the ideal full-scale output (20 mA). This is
the corrected ideal full-scale output:
11. Readjust zero and span adjustments for corrected outputs:
3.964 mA at –100 inH
2
O
20.108 mA at 300 inH
2
O
There is an uncertainty of ±0.5 percent of input reading per 1,000
psi associated with the span correction.
Zero
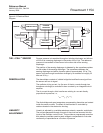
Zero shift with static pressure is not systematic. However, if the calibrated
range includes zero differential pressure, the effect can be trimmed out after
installation and with the unit at operating pressure.
0.75 %
1,000 psi
------------------------
1 200 psi 0.9% differential input=,×
0.9 % 100 inH
2
–× O 0.9 inH
2
O–=
0.9 inH
2
O–
400 inH
2
O input span
---------------------------------------------------------------- 0.225 % span–=
0.225 % 16 mA span×– 0.036 mA–=
4.00 mA 0.036 3.964 mA=–
0.9 % 300 inH
2
× O 2.7 inH
2
O=
2.7 inH
2
O
400 inH
2
O input span
---------------------------------------------------------------- 0.675 % span=
0.675 % 16 mA span× 0.108 mA=
20.00 mA 0.108 mA 20.108 mA=+