16
FINDING OPTIMAL SETTINGS
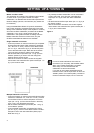
frequency response; see fig. 13. In the same manner, with
the cross-over frequency for the main speakers set too low
(cross-over freq. for the subwoofer too high), there will be
too much of an overlap between subwoofer and main
speakers, again resulting in incorrect overall frequency
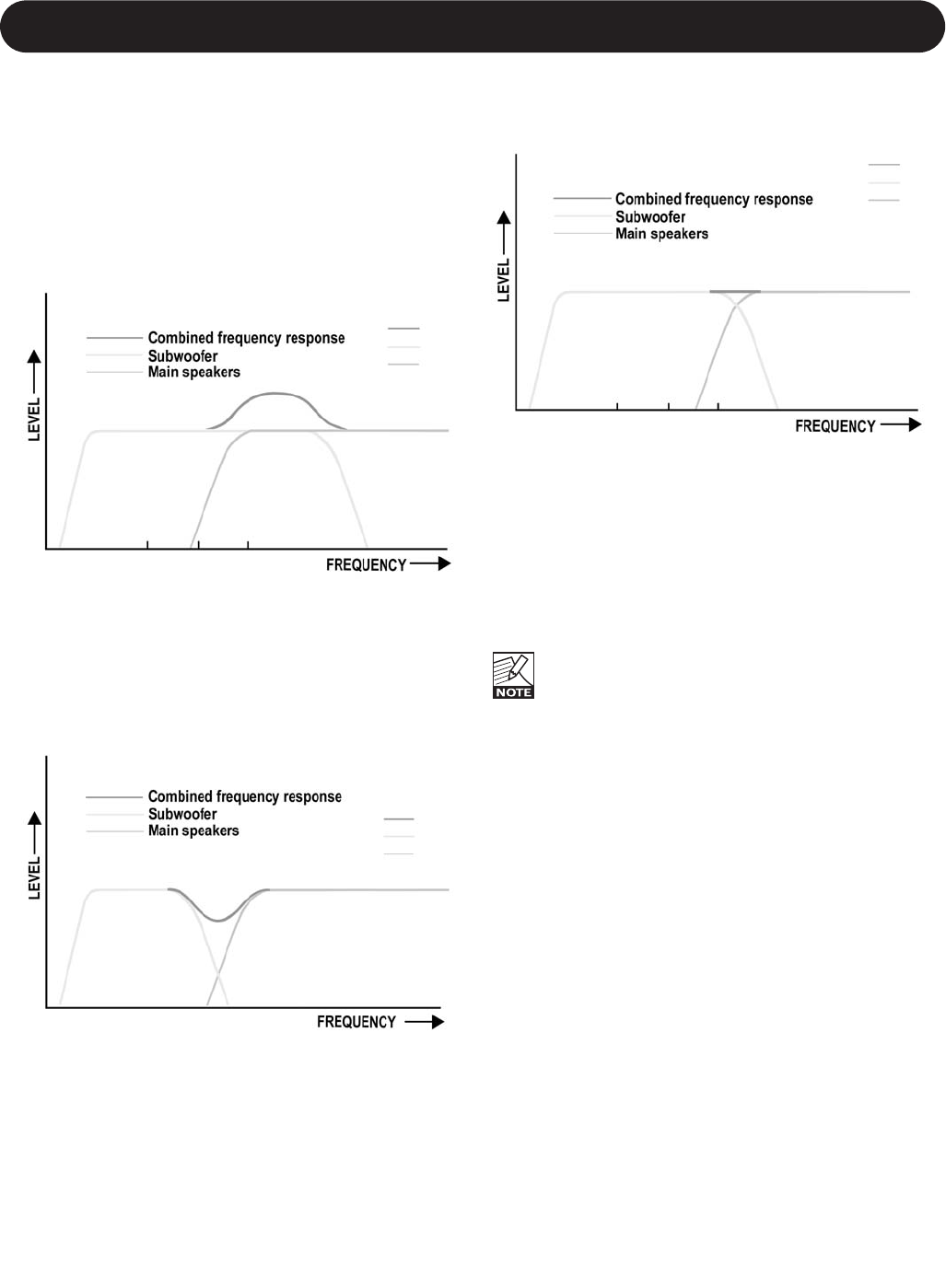
response; see fig. 14. Correct settings are illustrated in fig. 15.
Fig. 13
Subwoofer cross-over frequency set too high (main
speakers too low): Bump in frequency response.
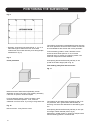
Fig. 14
Subwoofer cross-over frequency too low (main speakers
too high): Gap in frequency response
Fig. 15
Subwoofer & main speakers cross-over frequencies set
correctly: Smooth frequency response.
Many multi-channel processors and receivers provide
elaborate bass-management systems where the cross-over
frequency for both subwoofer and main speakers can be
set. If you are using such a bass-management system, you
can select the "Flat" setting on the subwoofers remote
control, as all filtering has been done by the bass-
management system. Carefully follow the instructions for
the amplifier/processor or receiver.
• If you are using your system's bass-management
system, ensure that the subwoofers cross-over
frequency hasn't been set to the same or lower
frequency compared to the setting chosen with the
bass management system.
• Selecting the correct frequency depends to a large
extend on the main speakers. Sometimes main
speakers are specifically intended to work with a
subwoofer. In such cases, the main speakers can
get damaged by a full-range amplifier signal. If in
doubt, check the instruction manual for the main
speakers for any restrictions or recommendations.
Of course it is possible to combine the subwoofer in a
system where the loudspeakers are being fed with a full-
range signal. In that case, setting the cross-over frequency
for the subwoofer depends very much on the natural roll-off
frequency in the bass of the main speakers. In general, a
large, floor-standing speaker will still have significant
Output in the deeper bass range, in which case the cross-
over frequency should be set to 60Hz. A small or very small
speaker will have less deep bass Output in which case the
setting should be 80Hz. or 100Hz. To find the correct
setting in such scenarios:
• Play a music track that has a significant amount of bass
over a large bass region. An instrument such as a
double-bass or bass-guitar is very suitable. Starting with
the "60" Hz position (first button left in row No. 3 in fig.
6), use this track to set the subwoofers relative volume
level.