ENGLISH
19
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Component video
Video signals with three channels of separate information
that makes up the picture. There are some types of
component video, such as Y/CB(Pb)/CR(Pr) and R/G/B.
Bitstream
The digital signal form of multichannel audio data (e.g., 5.1
channel) before it is decoded into its various channels.
Linear PCM
PCM stands for Pulse Code Modulation. Linear PCM is the
usual digital method without compression, used for audio
playback of audio CDs, DVD Videos, etc.
Title, Title number (DVD Video)
The title is the largest unit of the video/audio recording in
DVD Videos. Usually, the title corresponds to a movie of
video software or an album (or a piece) of music software.
Title numbers are sequential numbers assigned to titles.
Chapter, Chapter number (DVD Video)
Chapters are divisions, which are smaller than the titles, of
the contents recorded on DVD Videos. Every title is
composed of more than one chapter. Chapter numbers are
the sequential numbers assigned to the chapters in a DVD
Video.
Track number (CD)
Track numbers are used to designate the various sections of
a disc.
Folder (MP3 disc)
Folder is the largest unit of the contents recorded on MP3
discs.
File (MP3 disc)
Each material (song) is recorded on a file.
Files may be grouped into a folder by artist, album, category,
etc.
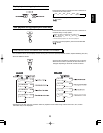
• DVD Video structure
• CD structure
• MP3 disc structure
On an MP3 disc, a folder can be a member of another folder,
creating hierarchical folder layers. If you are familiar with a
personal computer, you may easily understand the
hierarchical file/folder construction.
DVD Video
This refers to a high-density optical disc on which high-
quality pictures and sound have been recorded by means
of digital signals. Incorporating a new video compression
technology (MPEG-2) and high-density recording
technology. DVD Video enables esthetically pleasing full-
motion video to be recorded over long periods of time (for
instance, a whole movie can be recorded).
DVD Video has a structure consisting of two 0.6 mm thin
discs which are adhered to each other. Since the thinner the
disc, the higher the density at which the information can be
recorded, a DVD Video has a greater capacity than a single
1.2 mm thick disc. Since the two thin discs are adhered to
each other, there is the potential to achieve double-sided
play sometime in the future for even longer duration play.
MPEG
MPEG stands for Moving Picture Expert Group. It is regarded
as an international standard for compressing and restoring
digital video and audio signal. “MPEG” standards include
MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. Video CD and MP3 are
based on MPEG-1, while DVD Video is based on MPEG-2.
MP3
MP3 is an audio data reduction format, which stands for
MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3. Using MP3, you can achieve a data
reduction of about 1:10.
Aspect ratio (DVD Video)
The aspect ratio is the ratio between the vertical and
horizontal size of the picture displayed on a TV screen. The
aspect ratio of normal TV screen is 4:3 while that of the
wide-screen TV and HDTV screen is 16:9.
Subtitle (DVD Video)
Some DVD Videos contain the recording of more than one
subtitle languages. With these discs, this unit can select one
of the subtitle languages as desired during playback.
Angle (DVD Video)
Some DVD Videos contains scenes which have shot
simultaneously from multiple camera angles. With these
discs, the same scene can be viewed from each of these
different angles.
Interlaced scan
In the conventional video system, a picture is shown on the
screen in two halves. The interlaced scanning system places
lines of the second half of the picture in-between lines of the
first half of the picture.
Progressive scan
Progressive scanning displays all the horizontal lines of a
picture at one time, as a single frame.
Composite video
A single video signal commonly used in most consumer
video products that contains all luminance, color, and
synchronization information.
S-video
A video signal which improves picture quality over the
standard composite video signal.