CALIBRATION AND REPAIR
19
The other two fuses are in-line with the
batteries. These fuses will blow if the rear
panel ±12 VDC supplies are shorted, or if
the unit sources or draws excessive current
to or from the batteries.
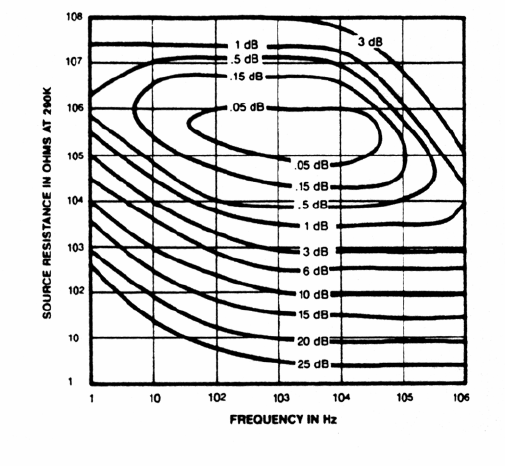
NOISE CONTOURS
The noise contours (shown upper right) plot
the noise figure as a function of source
impedance and frequency. Noise Figure
(NF) is defined as:
• NF = 20 log (Output noise / (Gain X
Source Thermal Noise)
A low noise figure means that the output
noise is dominated by the thermal
(Johnson) noise of the source. A high noise
figure indicates that the amplifier's output
noise is dominated by the amplifier's own
noise, which is much larger than the thermal
noise of the source.
The NF gets worse for low source
resistances because the source's thermal
noise gets very small, while the amplifier's
input voltage noise stays relatively constant.
The NF gets worse for low frequencies and
low source resistances because the
amplifier's "1/f" noise is large relative to the
thermal noise of the source.
The NF gets worse for large source
impedances and high frequencies because
the signal is attenuated (hence the gain
reduced) by the shunting capacitance of the
input.
Under no circumstances will adding source
resistance reduce the amplifier's output
noise! While this does improve the NF, it
does so by making the source so noisy that
the amplifier is quiet in comparison.