March 1994 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Triple video output amplifier TDA6103Q
Dissipation
Regarding dissipation, distinction must first be made between static dissipation (independent of frequency) and dynamic
dissipation (proportional to frequency).
The static dissipation of the TDA6103Q is due to voltage supply currents and load currents in the feedback network and
CRT.
The static dissipation equals:
P
stat
= V
DD
× I
DD
− 3 × V
oc
× (V
oc
/R
fb
− I
OC
)
R
fb
= value of feedback resistor.
I
OC
= DC-value of cathode current.
The dynamic dissipation equals:
P
dyn
= 3 × V
DD
× (C
L
+ C
fb
+ C
int
) × f
i
× V
o(p-p)
×δ
C
L
= load capacitance.
C
fb
= feedback capacitance.
C
int
= internal load capacitance (≈4 pF).
f
i
= input frequency.
V
o(p-p)
= output voltage (peak-to-peak value).
δ = non-blanking duty-cycle.
The IC must be mounted on the picture tube base print to minimize the load capacitance (C
L
).
(1) All pins have an energy protection for positive or negative overstress situations.
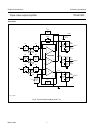
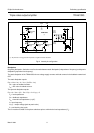
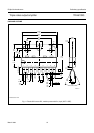
Fig.10 Internal pin configuration.
MGA971
from
input
circuit
V
bias
7,8,9
5
to
differential
stage
to
differential
stage
to
differential
stage
from
input
circuit
1,2,3
to
differential
stage
TDA6103Q
46
V
DD
GND
(1)