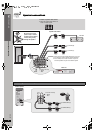
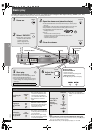
RQT8779
13
Product Service / Glossary
Product Service
1. Damage requiring service—The unit should be serviced by qualified service personnel if:
(a) The AC power supply cord or AC adaptor has been damaged; or
(b) Objects or liquids have gotten into the unit; or
(c) The unit has been exposed to rain; or
(d) The unit does not operate normally or exhibits a marked change in performance; or
(e) The unit has been dropped or the cabinet damaged.
2. Servicing—Do not attempt to service the unit beyond that described in these operating instructions. Refer all other servicing to authorized servicing
personnel.
3. Replacement parts—When parts need replacing ensure the servicer uses parts specified by the manufacturer or parts that have the same
characteristics as the original parts. Unauthorized substitutes may result in fire, electric shock, or other hazards.
4. Safety check—After repairs or service, ask the servicer to perform safety checks to confirm that the unit is in proper working condition.
The servicer will require all components to service your system.
Therefore, should service ever be necessary, be sure to bring the entire system.
For product information or assistance with product operation, refer to “Customer Services Directory” on page 38.
Decoder
A decoder restores the coded audio signals on DVDs to normal. This is
called decoding.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals developed by Dolby
Laboratories. Apart from stereo (2-channel) audio, these signals can also
be multi-channel audio. A large amount of audio information can be
recorded on one disc using this method.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie theaters around the world.
There is good separation between the channels, so realistic sound effects
are possible.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the lowest level of sound that
can be heard above the noise of the equipment and the highest level of
sound before distortion occurs.
Frame still and field still
Frames are the still pictures that go together to make a moving picture.
There are about 30 frames shown each second.
One frame is made up of two fields. A regular television shows these
fields one after the other to create frames.
A still is shown when you pause a moving picture. A frame still is made up
of two alternating fields, so the picture may appear blurred, but overall
quality is high.
A field still is not blurred, but it has only half the information of a frame still
so picture quality is lower.
I/P/B
MPEG 2, the video compression standard adopted for use with
DVD-Video, codes frames using these 3 picture types.
I: Intra coded picture
This picture has the best quality and is the best to use when adjusting
the picture.
P: Predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated based on past I- or P-pictures.
B: Bidirectionally-predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated by comparing past and future I- and
P-pictures so it has the lowest volume of information.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
This is a system used for compressing/decoding color still pictures. If you
select JPEG as the storage system on digital cameras, etc., the data will
be compressed to 1/10–1/100 of its original size. The benefit of JPEG is
less deterioration in picture quality considering the degree of
compression.
Linear PCM (pulse code modulation)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar to those found on CDs.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer 3)
An audio compression method that compresses audio to approximately
one tenth of its size without any considerable loss of audio quality.
Playback control (PBC)
If a Video CD has playback control, you can select scenes and
information with menus.
Progressive/Interlaced
NTSC, the video signal standard, has 480 interlaced (i) scan lines,
whereas progressive scanning uses twice the number of scan lines. This
is called 480p.
Using progressive output, you can enjoy the high-resolution video
recorded on media such as DVD-Video.
Your television must be compatible to enjoy progressive video.
Sampling frequency
Sampling is the process of converting the heights of sound wave (analog
signal) samples taken at set periods into digits (digital encoding).
Sampling frequency is the number of samples taken per second, so larger
numbers mean more faithful reproduction of the original sound.
WMA (Windows Media
TM
Audio)
WMA is a compression format developed by Microsoft Corporation. It
achieves the same sound quality as MP3 with a file size that is smaller
than that of MP3.
Product information
Glossary