6
Sealed Bandpass Enclosure
Sealed bandpass enclosures enclose both sides of the woofer(s). An
airtight enclosure is built around the front and back of the woofer and
one chamber is ported to a specific frequency.
CALCULATING (NET) INTERNAL ENCLOSURE VOLUMES
When constructing any type of enclosure, you must be aware that the
outside dimensions DO NOT represent the true (Net) volume inside.
Such things as woofers, ports, thickness of enclosure material, dividing
walls, and any internal bracing will reduce the total amount of the
actual air space available. The following worksheet has been designed
to provide you with the necessary steps to accurately calculate the
absolute (Net) internal volume of any given enclosure.
Calculating Cylindrical Port Volume
1. Measure the outside diameter of the port and divide by 2 for the
radius.
2. Square the radius and multiply by 3.14 (π) to arrive at outside port
area.
3. Multiply the area by the length of the port inside the enclosure for
the port volume.
outside
diameter
length inside
enclosure
Pros Cons
• High power handling
within the operating
frequencies
• Very high output within
the range of the oper-
ating frequencies
• Low power handling
beyond the tuning
frequency
• Poor to moderate
transient response
• Poor low frequency
extension
Sealed
Bandpass
(SBP)
7
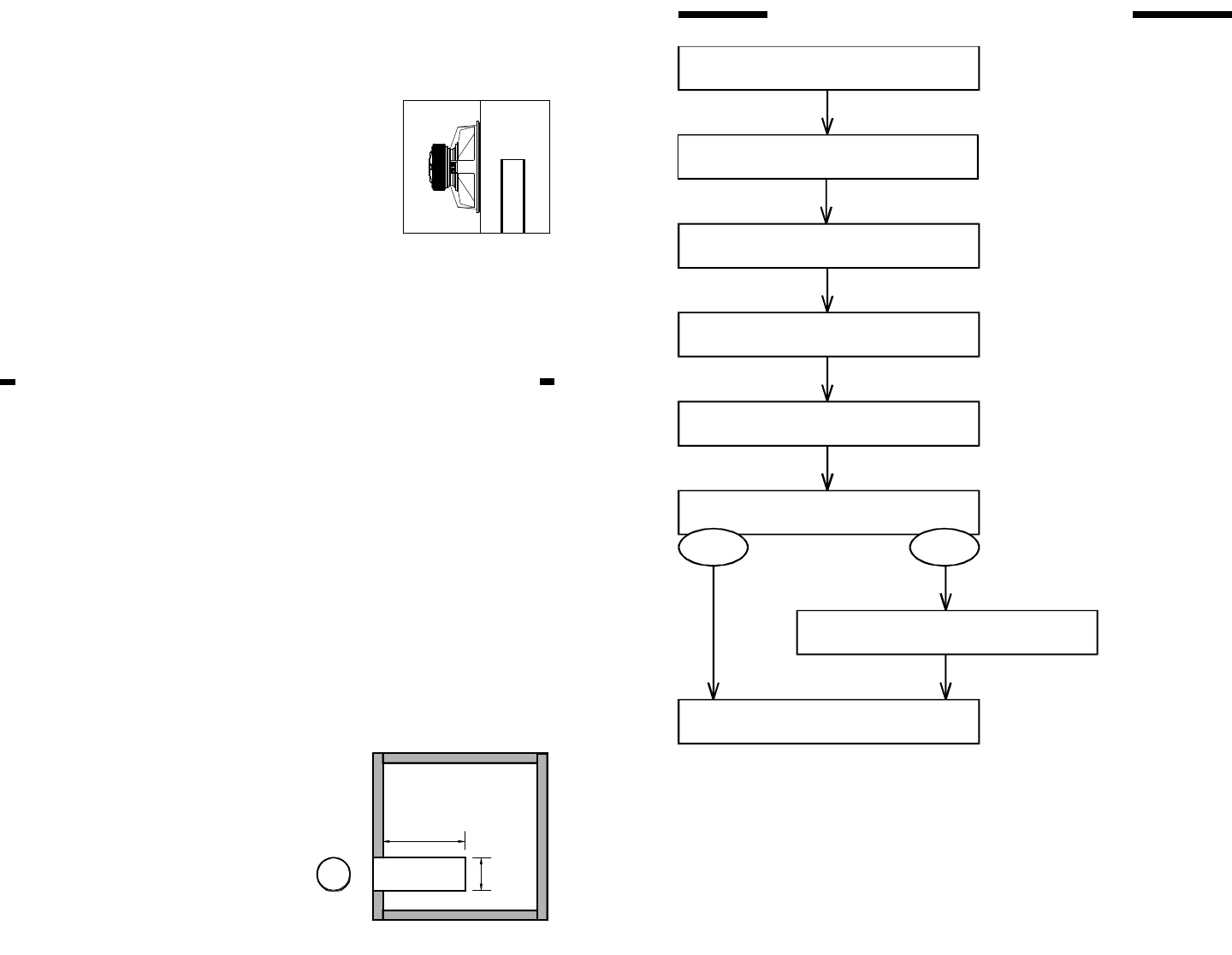
Measure maximum possible dimensions
Multiply wall thickness by 2
Subtract this from each dimension to
arrive at Gross Internal Dimensions
Multiply LxWxD to arrive at
Gross Internal Volume
Deduct Vf (volume of the speaker frame)
from Gross Internal Volume
Braces?
No Yes
Calculate brace volume and deduct
from Gross Internal Volume
Deduct Vf (volume of the speaker frame)
from Gross Internal Volume
You are at Net Internal Volume
in cubic inches (in )
3
To convert to LITERS:
Divide in by 61.03
To convert to CUBIC FEET:
Divide in by 1728
3
3
ENCLOSURE VOLUME FLOWCHART
