Additional Information 45
EN
Additional Information
Tips on radio waves
What is SSB (Single Side Band)?
SSB is very popular among ham and
business radio transmissions, and is
commonly used in many amateur
bands because of its superiority in
signal intelligibility. Its impressive
signal intelligibility is achieved with
minimum interferences when
compared to DSB (Double Side Band)
owing to its half bandwidth structure.
In general, SSB transmissions employ
the USB (Upper Side Band)
modulation, while amateur band
transmissions below 10 MHz employ
the LSB (Lower Side Band)
modulation.
Conventional radios without a BFO
(Beat Frequency Oscillator) circuit
cannot receive SSB transmissions
successfully. This unit can receive SSB
transmissions successfully with the
built-in BFO (Beat Frequency
Oscillator) circuit.
What is CW (Continuous Wave)?
CW is also popular among ham and
business radio transmissions. Unlike
other signals, the amplitude of a
carrier is not modulated for CW
transmissions. CW transmissions
convey information by interrupting
the carrier and use Morse code as a
means of communication.
This unit can receive CW
transmissions successfully with the
built-in BFO (Beat Frequency
Oscillator) circuit as beat sound only.
To fully comprehend the information
transmitted by CW transmissions, an
understanding of the Morse code is
prerequisite.
LSB
USB
Carrier
Amplitude
Frequency
What is synchronous detection?
There are two underlying obstacles in
optimum AM reception: distortions due
to fading and interferences from adjacent
broadcast stations.
The synchronous detection is effective in
solving these obstacles.
Distortions due to fading are generally
caused by over-modulation which occurs
when a carrier component of the
received signal is attenuated along the
way. The synchronous detection circuit
of this unit generates a pure carrier
frequency with no level variation which
is ideally synchronized with the original
carrier to compensate for the attenuated
carrier component, thus dramatically
reducing distortion.
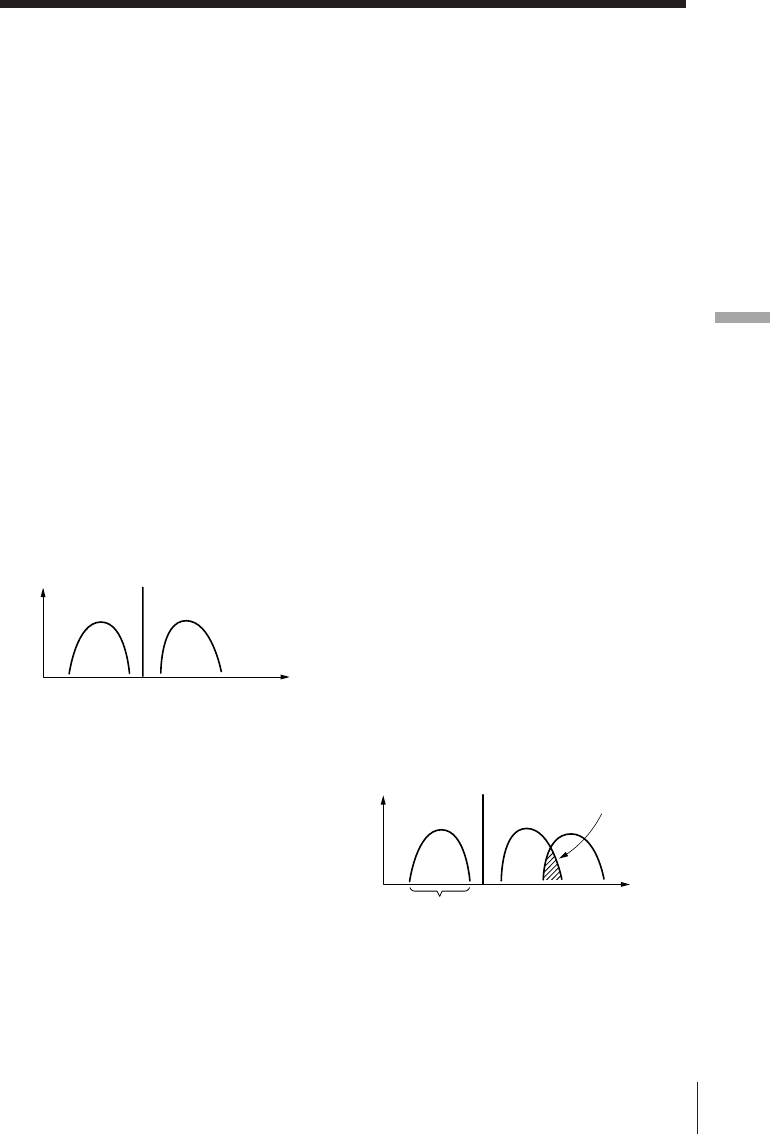
Likewise, AM (LW, MW, and SW)
broadcast generally employs DSB
(Double Side Band) signals for
transmissions in which the modulated
signals are transmitted using both the
upper and lower side bands (USB and
LSB). In most cases, one of the side bands
is affected by interferences from adjacent
broadcast stations (i.e., beats). The
synchronous detection circuit of this unit
extracts one of the two sides (USB or
LSB) of the DSB (Double Side Band)
signal which is free from interferences.
This allows clear reception without the
interferences from adjacent broadcast
stations.
This side is received only.
USBLSB
Carrier
Interferences
from adjacent
broadcast
stations.