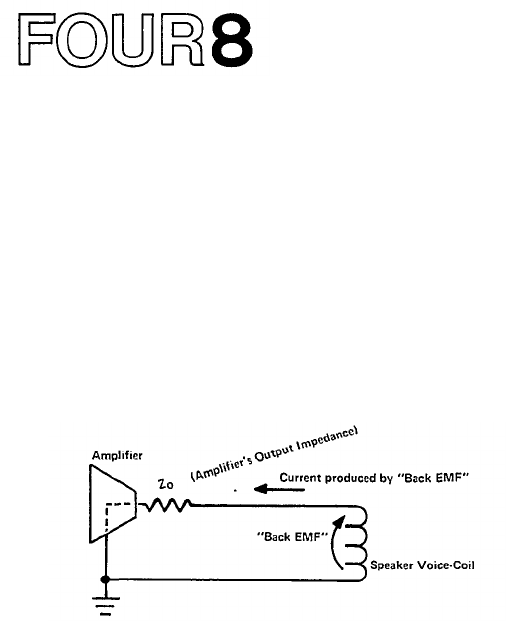
During the "overshoot" movement, the voice coil of
the loudspeaker interacts with the loudspeaker's magnetic
assembly to produce a voltage called "back E.M.F."
(electro-motive force). This action is similar to the
operation of a dynamic microphone. If the amplifier's
output impedance is low, this "back E.M.F." voltage is
shunted through the amplifier's output circuits to
ground, and back to the voice coil. Since the path from
the voice coil, through the amplifier's output circuits,
and back to the voice coil is a complete circuit, a
current flows in the voice coil. This current, causes
the voice coil to act like an electro-magnet; the electro-
magnet (voice coil) interacts with the magnetic assembly
of the loudspeaker, and the unwanted overshoot is
reduced (a magnetic braking action).
Fig. 31 - Current produced by "Back EMF" follows path
through Amplifier's Output Impedance to speaker-coil.
If the amplifier's output impedance is low (con-
siderably less than the impedance of the loudspeaker
voice coil), this damping action is limited only by the
resistance of the voice coil combined with the resistance
of the speaker lead wires. While the value of a high
damping factor in reducing cone overshoot is disputed,
the P-2200's high damping factor is evidence of good
overall engineering design.