8 9
Low Mid Contour Frequency: A shelving filter can be set to the flat anechoic response or set to shelve at frequencies of 800Hz,
400Hz, or 200Hz in combination with the low mid contour amplitude (below) to correct half space (pi/2), quarter space (pi/4)
and very difficult close field boundary conditions (pi/8 space).
Low Mid Contour: a shelving filter can be set to a flat anechoic response or to -2dB, -4dB, -6dB or -8dB in combination with
the low mid contour frequency (above) to correct mid, near and close field listening positions compared with free space, far
field conditions.
Figures 3, 4 and 5 below show the range of amplitude settings at 800Hz, 400Hz and 200Hz and the DIP switch settings. DIPs
5 to 8 (inclusive) control the amplitude responses and switches 9 and 10 control the frequency at which the shelving starts. All
other DIPs are shown in the 'Flat' position.
Baffle Step Effect: Both low mid frequency and low mid contour are used together to correct for the baffle step effect. the baffle
step effect is a well known property of speakers and is caused by a change in air load on the moving diaphragm at a frequency
dependant on the effective size of the baffle or cabinet frontal area compared with the wavelength of the sound being reproduced.
Most speakers are designed to have a flat amplitude and phase response over the audio band in anechoic or 'free field'
conditions where there are no boundary walls close to the bass drive unit. When the speaker is placed against a wall, in a
corner, on a mixing console or on a table adjacent to a PC editor the wall boundaries effectively increase the baffle size. This
produces a boost in the frequency band around 100 to 800 Hz depending on the effective size and proximity of the boundary
surfaces, the size of the bass driver and the distance of the listener from the source.
More at: Olson, H. F. "Direct Radiator Loudspeaker Enclosures" Journal of the Audio Engineering Society Vol. 17, No. 1, 1969
October, pp.22-29
There are many more references to these effects by searching the web for 'Baffle Step Effect'.
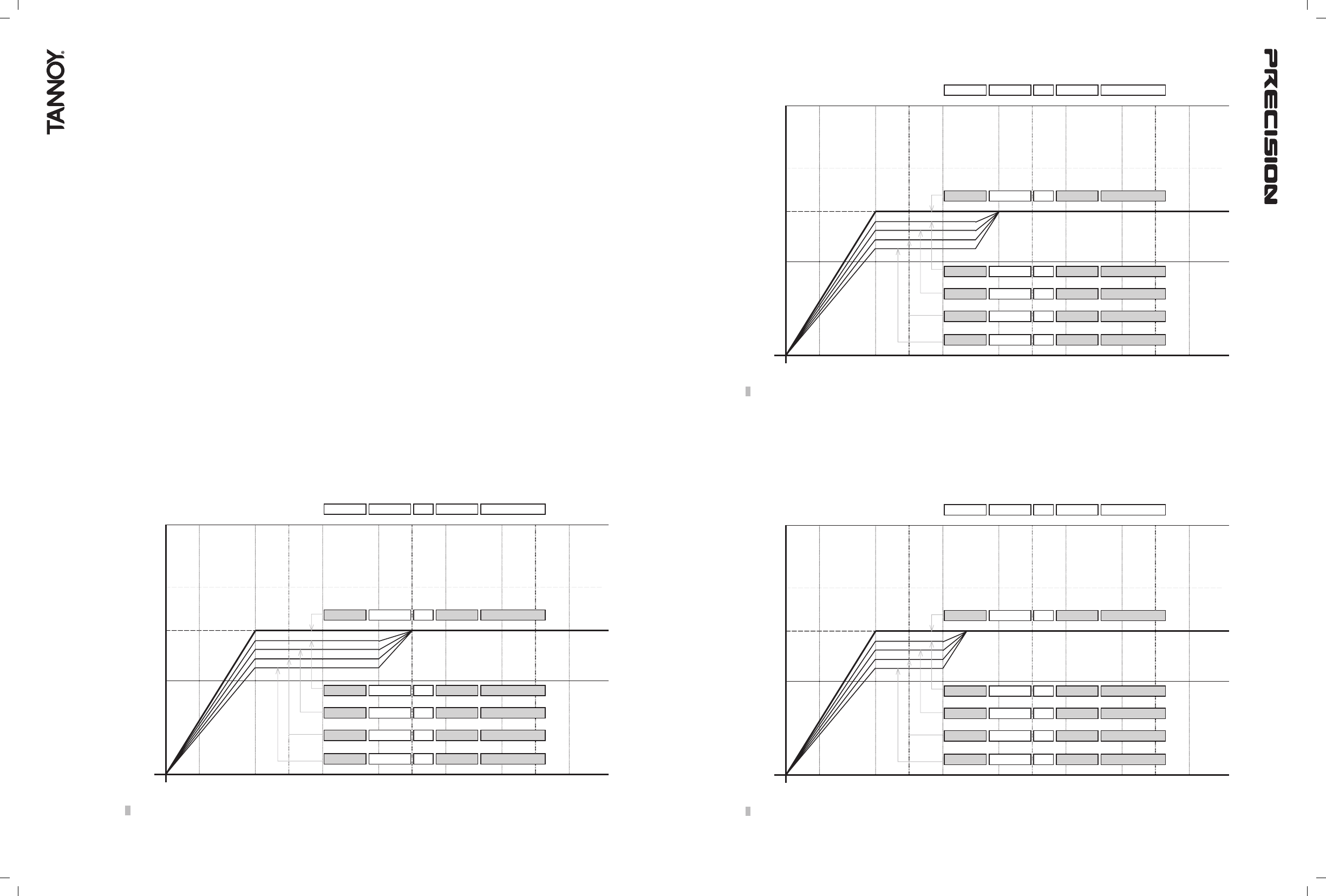
Fig. 3. DIP switches 5 to 8 control amplitude, 9 & 10 control frequency - set here to 800Hz. All other DIPs set to 'flat'.
10Hz 100Hz 1Khz 10kHz
-10dB
+10dB
0dB re 2.8v
@ 1 metre
500Hz 5kHz200Hz 2kHz 20kHz20Hz 50Hz
LF EQ Low Mids Hz Up Mid Highs
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Diagramatic View of EQ Dip Switches: Baffle Step Filters, Low Mids, 800Hz
20 way DIP Switch Bank (4+4+2+4+6)
Fig. 5. DIP switches 5 to 8 control amplitude, 9 & 10 control frequency - set here to 200Hz. All other DIPs set to 'flat'.
10Hz 100Hz 1Khz 10kHz
-10dB
+10dB
0dB re 2.8v
@ 1 metre
500Hz 5kHz200Hz 2kHz 20kHz20Hz 50Hz
LF EQ Low Mids Hz Up Mid Highs
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Diagramatic View of EQ Dip Switches: Baffle Step Filters, Low Mids, 200Hz
20 way DIP Switch Bank (4+4+2+4+6)
Fig. 4. DIP switches 5 to 8 control amplitude, 9 & 10 control frequency - set here to 400Hz. All other DIPs set to 'flat'.
10Hz 100Hz 1Khz 10kHz
-10dB
+10dB
0dB re 2.8v
@ 1 metre
500Hz 5kHz200Hz 2kHz 20kHz20Hz 50Hz
LF EQ Low Mids Hz Up Mid Highs
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Diagramatic View of EQ Dip Switches: Baffle Step Filters, Low Mids, 400Hz
20 way DIP Switch Bank (4+4+2+4+6)