C M Y CM MY CY CMY K
19
TM
9.0: EQUALISATION
VNET“ loudspeakers are designed to need no equalisation or correction to overcome system limitations. As a result, they
will only need equalisation to compensate for difficult acoustic environments.
Over equalisation can reduce system headroom, and introduce phase distortion resulting in greater problems than cures. If
equalisation is required then it should be applied gently and smoothly. VNET“ full range loudspeakers are point source, phase
coherent designs and violent equalisation will be detrimental to the overall sound quality.
When a loudspeaker is used in close proximity to another, comb filtering effects can create coverage problems; comb filtering
creates an uneven frequency response across the coverage area due to constructive and destructive interference effects
between the sources. The amount of comb filtering is affected by the spacing of the relative sound sources. Minimising this
effect cannot be cured by equalisation (see the following section for more details).
10.0: ARRAYING
As discussed in the previous section, comb filtering cannot be cured by equalisation. Small alterations to loudspeaker positions
can have the effect of minimising problematic combing frequencies. Arrays should be constructed so that the individual coverage
patters of each loudspeaker combine with minimal overlap. The design of the VNET“ cabinet greatly simplifies the creation
of effective arrays, allowing seamless wide horizontal coverage (140deg for VNET12/VNET300 & 130deg for VNET12HP/V15)
using two loudspeakers without the need for tedious experimentation.
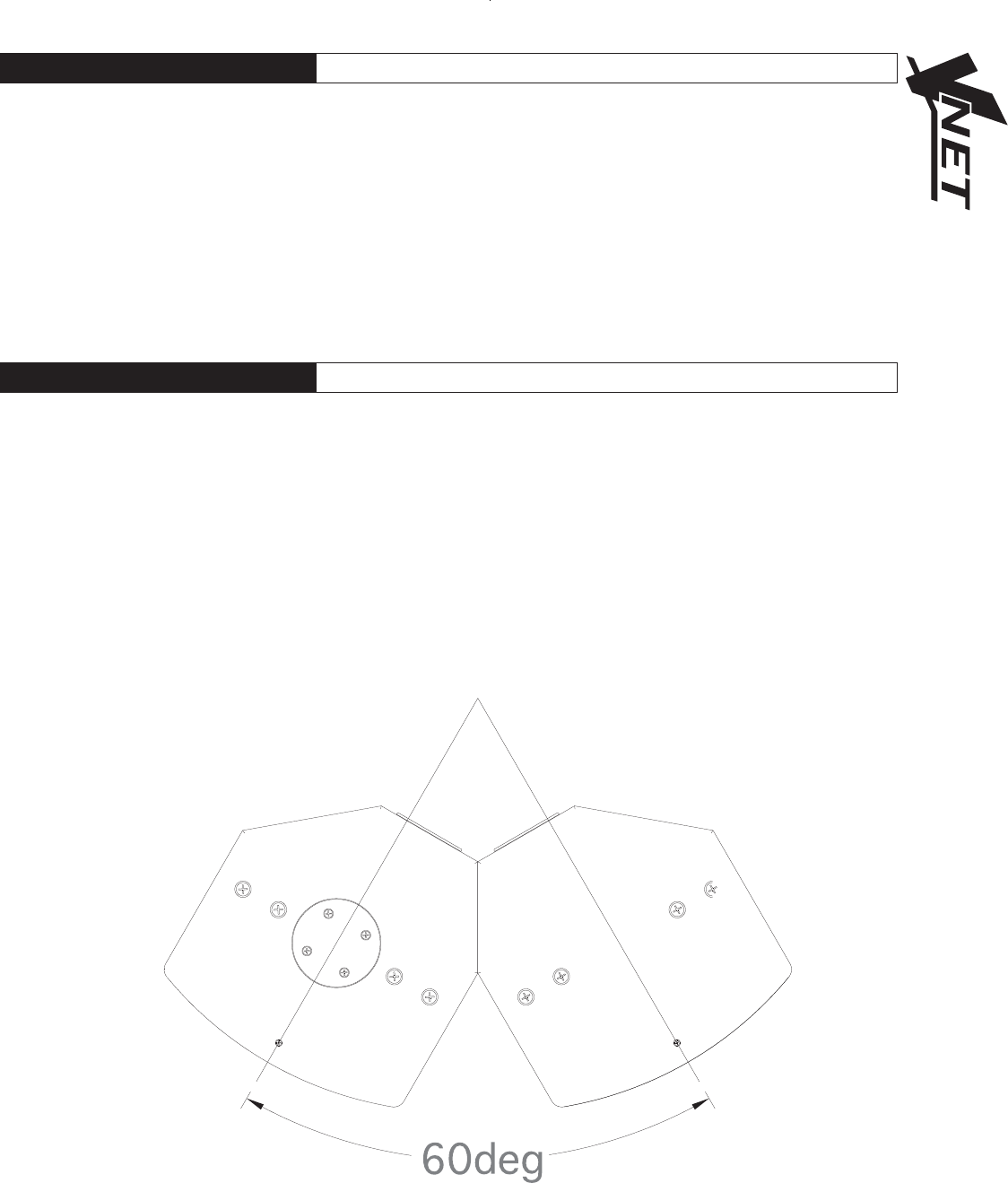
By placing the VNET12, VNET12HP, & VNET300 cabinets with the 30 degree angled rear panels together, minimal dispersion
pattern overlap is achieved, guaranteeing an extraordinarily smooth transition.
In many applications the 90-degree (75 — degree on the VNET12HP/V15) dispersion pattern may be sufficient in the horizontal
plane.
It is also possible to stack the cabinets vertically using the above method, say for use in a central cluster, where greater vertical
dispersion is required.
As shown in the above diagram, one of the VNET“ cabinets is inverted to allow the optimum splay angle to be achieved. The
grill can be simply removed from this cabinet and be replaced in the correct orientation. The grill is held in position by the two
fixing screws on the top and bottom lips of the cabinet.


















