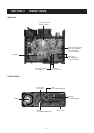
4 - 1
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
4-1-1 ANTENNA SWITCHING CIRCUIT
(MAIN UNIT)
Received signals passed through the low-pass filter (L44,
L47, L48, L51, C190, C197, C203, C208, C210, C217,
C218). The filtered signals are applied to the 1/4 λ type
antenna switching circuit (D16, D19).
The antenna swtiching circuit functions as a low-pass filter
while transmitting. However, its impedance becomes very
high while D16 and D19 are turn ON. Thus transmit signals
are blocked from entering the receiver circuits. The antenna
switching circuit employs a 1/4 λ type diode swtiching sys-
tem. The passed signals are then applied to the RF amplifi-
er circuit.
4-1-2 RF CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The RF circuit amplifies signals within the range of frequen-
cy coverage and filters out-of-band signals.
The signals from the antenna switching circuit are applied to
the limitter (D15), and are then passed through the band-
pass filter (D13, L43, C183, C182). The filtered signals are
amplified at the RF amplifier (Q27), then applied to the 1st
mixer circuit after out-of-band signals are suppressed at the
bandpass filter (D9–D11).
D9–D11, D13 employ varactor diodes that track the band-
pass filters and are controlled by the T1–T3 signals from the
D/A convertor (IC5, pins 10, 11, 23). These diodes tune the
center frequency of an RF passband for wide bandwidth
receiving and good image response rejection.
4-1-3 1ST MIXER AND 1ST IF CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signal to a fixed
frequency of the 1st IF signal with a PLL output frequency.
By changing the PLL frequency, only the desired frequency
will pass through two crystal filters at the next stage of the
1st mixer.
The signals from the RF circuit are mixed at the 1st mixer
(Q19) with a 1st LO signal coming from the VCO circuit to
produce a 21.70 MHz 1st IF signal.
The 1st IF signal is applied to two crystal filters (FI3 and FI4)
to suppress out-of-band signals. The filtered 1st IF signal is
applied to the IF amplifier (Q16), then applied to the 2nd
mixer circuit (IC4, pin 16).
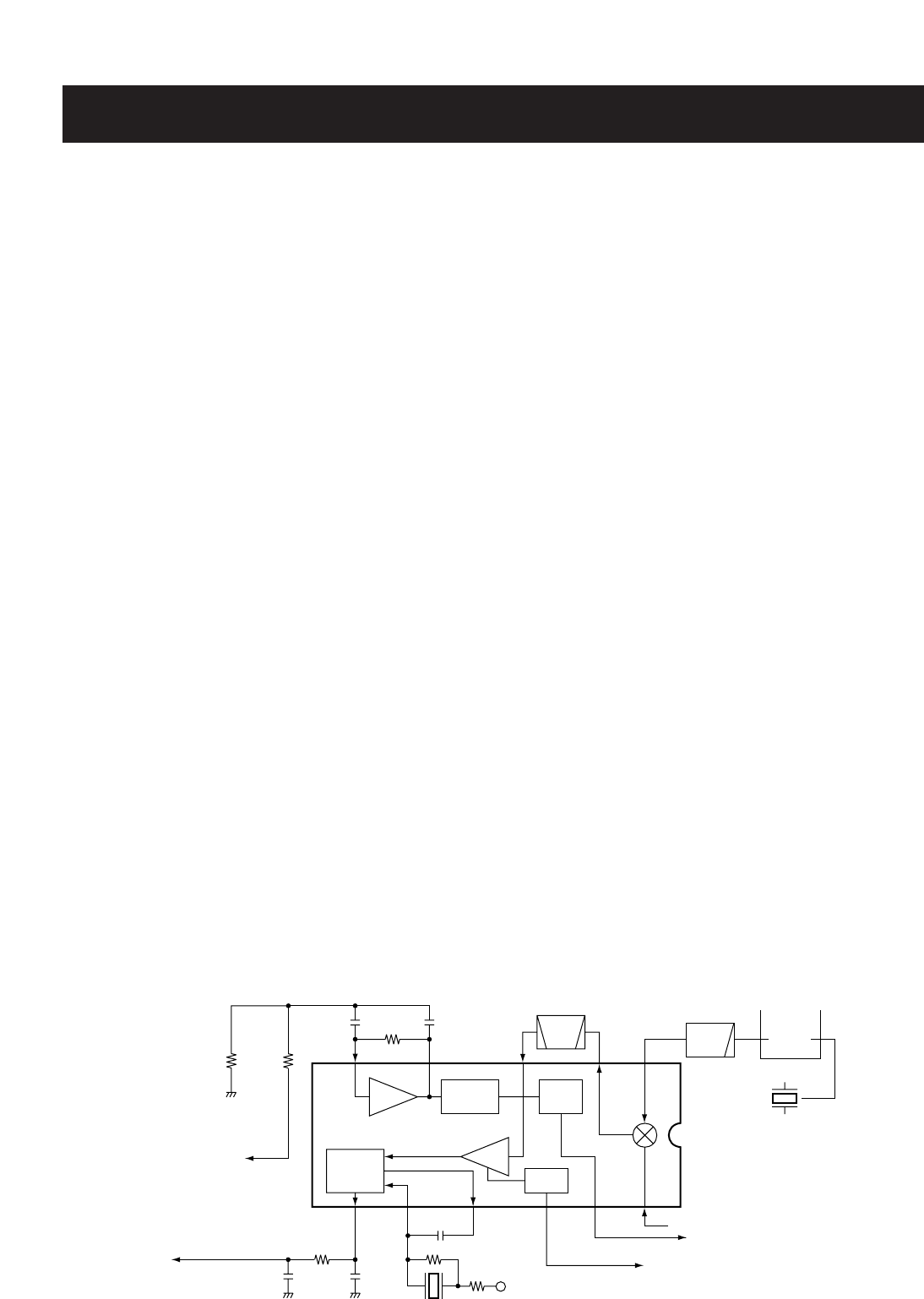
4-1-4 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The 2nd mixer circuit converts the 1st IF signal to a 2nd IF
signal. A double conversion superheterodyne system (which
converts receive signal twice) improves the image rejection
ratio and obtain stable receiver gain.
The 1st IF signal from the IF amplifier is applied to the 2nd
mixer section of the FM IF IC (IC4, pin 16), and is mixed with
the 2nd LO signal to be converted to a 450 kHz 2nd IF sig-
nal.
The FM IF IC contains the 2nd mixer, limiter amplifier, quad-
rature detector and active filter circuits. A 21.25 MHz 2nd LO
signal is produced at the PLL circuit.
The 2nd IF signal from the 2nd mixer (IC4, pin 3) passes
through a ceramic filter (FI1; When wide is selected, F2;
When Narrow is selected. (Narrow is [USA] version only.)) to
remove unwanted heterodyned frequencies. It is then ampli-
fied at the limiter amplifier (IC4, pin 5) and applied to the
quadrature detector (IC4, pins 10, 11) to demodulate the 2nd
IF signal into AF signals.
4-1-5 AF CIRCUIT (MAIN AND LOGIC UNITS)
The AF amplifier circuit amplifies the demodulated AF sig-
nals to drive a speaker.
AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC2, pin 9) are applied to the
analog swtich (LOGIC UNIT; IC6, pin 1) via the high pass fil-
ter (IC3c, pins 9, 8). The output signals from pin 11 are
applied to the volume adjustment pot (LOGIC UNIT; R31).
The signals are applied to the AF power amplifier (IC9, pin
1) after passing through the AFmute swtich (Q29).
Mixer
16
Limiter
amp.
2nd IF filter
450 kHz
PLL IC
IC1
X1
21.25 MHz
IC4 TA31136F
12
1st IF from the IF amplifier (Q16)
"SD" signal to the CPU pin 97
11109
87 5 3
AF signal "DETO"
R5V
X2
R55
C84
C85
R64R59
R71
"SQLIN" signal from the
D/A convertor (IC5, pin 214
R73
C105 C101
C116
2
16 1
Active
filter
FI2
Noise
detector
FM
detector
13
"NOIS" signal to the CPU pin 19
RSSI
Noise
comp.
R63
LPF
• 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS