9
8
ACE technology
The laws of physics dictate that to get good bass
extension out of a loudspeaker you need a large
enclosure volume, and to get high output levels you
need to move a lot of air. This is why the more
expensive loudspeaker systems have large or
multiple bass drivers and big enclosures.
Many potential solutions to the enclosure size
problem have been tried over the years, but KEF’s
ACE technology is the one which genuinely works
and is useable in production systems.
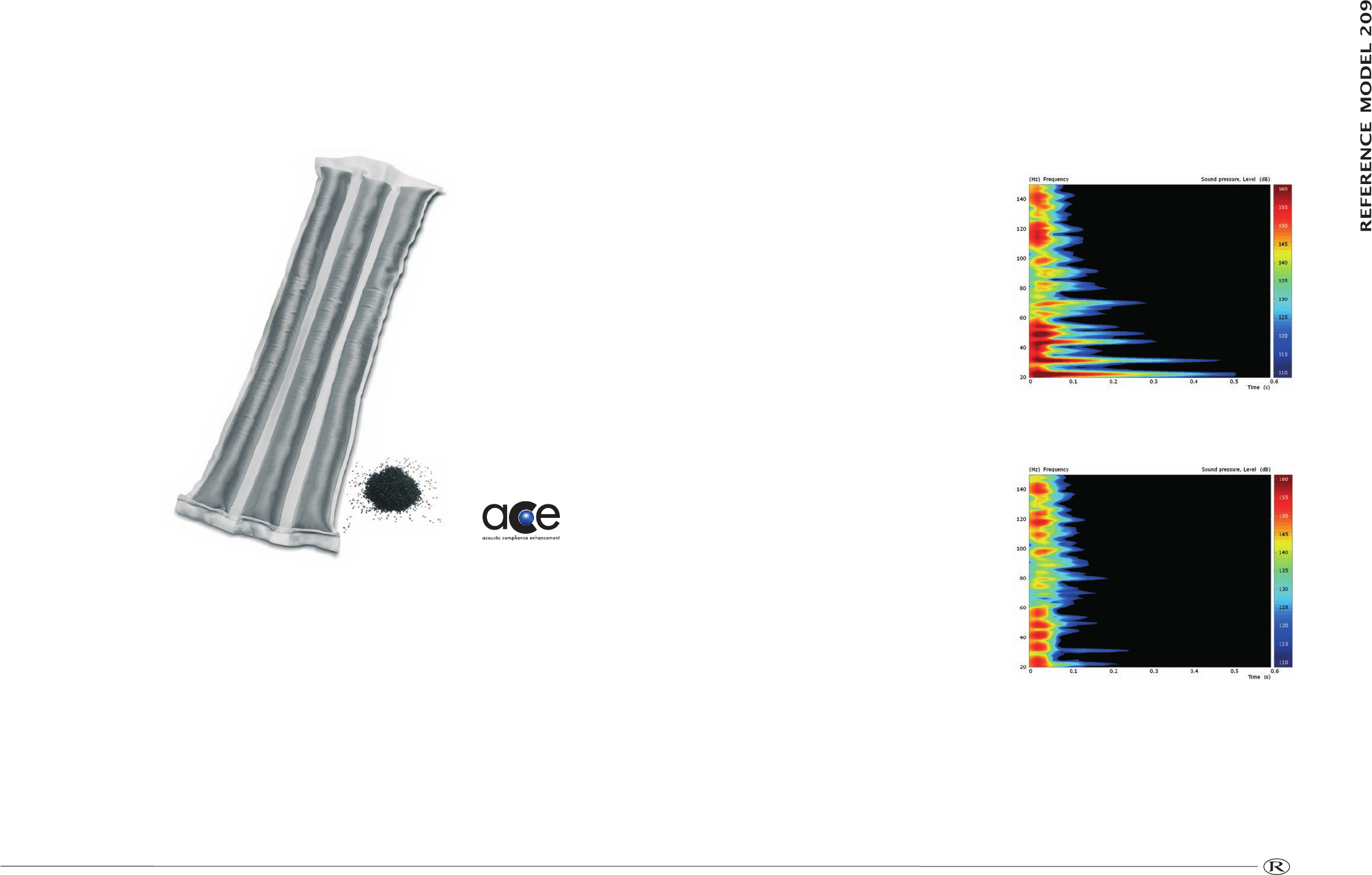
ACE stands for Acoustic Compliance
Enhancement. Granules of activated carbon are
packed into porous fabric tubes and fitted inside
the loudspeaker enclosure. These carbon
granules are highly porous with many pores,
macropores and micropores giving them an
incredibly high surface area. ACE works by
a process called ‘adsorption’. It’s a physical
process whereby the granules of
activated carbon continually work to
reduce the acoustic pressure within
an enclosure. When the drive unit
cone moves inwards the air
pressure inside the enclosure
increases. This triggers the
carbon granules to pull air
molecules onto the
surface of the material
by the weak, gravity
type, Van de Waals force.
This has the effect of reducing the overall air
pressure inside the enclosure. When the cone
moves out, and acts to expand the air inside the
enclosure and reduce its pressure, the granules
‘give out’ air molecules, again reducing
the pressure change. A smaller
change in the internal
enclosure pressure
is equivalent to
having a larger enclosure
volume. So by placing
modules of activated
carbon granules inside the
enclosure we are getting the
acoustic performance of an
enclosure with a much larger
physical volume.
The adsorption process is linear
and reversible, there is no distortion
introduced because of the operation
of the carbon granules. In fact, the
bass quality of ACE loaded enclosures
is consistently admired by audiophiles
for its clarity and detail.
Room Correction
The listening room has a major impact on the
sound of loudspeakers, particularly at low
frequencies. In this region, standing wave
resonances in the room result in large peaks
and dips in the loudspeaker response.
It is very difficult to compensate for the effect
of the room. This is mainly because the effect is
not uniform but is different at every location in
the room. If one were to perfectly correct the
subwoofer response in one location it would
inevitably become worse elsewhere.
KEF engineers made the discovery that the
acoustic behaviour of the room can be
separated into two distinct parts, one part that
describes all of the spatial variation in the room
and a second part that describes the resonant
behaviour in the room. As this second
resonant part is independent of the
loudspeaker and listener positions it can be
electronically corrected for all locations in the
room simultaneously.
KEF has developed an innovative room
correction system that analyses the acoustical
characteristics of the room and then designs a
digital compensation filter to optimally correct
the subwoofer response. This method of room
correction gives a very significant audible
improvement in the subjective performance
of the bass, it sounds tighter and more defined.
Best of all, it works wherever you are in
the room.
An additional benefit of this method of room
correction is that it makes positioning of the
subwoofer much simpler. Traditionally it is
advisable to position subwoofers away from
walls and corners as these locations result in
very strong excitation of the room resonances.
With the KEF room correction system,
however, the resonances are electronically
compensated and there is no problem with
locating the subwoofer close to walls or in the
corner of a room.
Before room correction.
After room correction.
K7262 REF 209208 Combined Manual_v2 12/2/08 12:40 Page 8