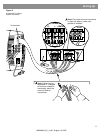
7
Setting Up
Front left and right cube speaker arrays
The front left and right cube speaker arrays create a sound image wider than the screen that
seems natural to viewers sitting anywhere in the room. You can place the cube speaker arrays
near a TV screen with no picture interference. Place the front cube speaker arrays on either
side of your TV, at least 6 feet (2m), or as much as 15 feet (5m) apart (see Figure 2).
Rear cube speaker arrays
The rear, or surround cube speaker arrays add discrete sounds and special effects that
expand the visual image, bringing the viewer into the center of the action. The rear cube
speaker arrays may carry dialogue as well.
• Position the left and right rear cube speaker arrays to allow the sound to reach the viewer
from both sides, rather than from directly behind (see Figure 2).
• Place the rear cube speaker arrays at ear height (when seated) or higher, if possible.
• Rotate the top and bottom sections of the rear cube speaker arrays to direct the sound to
the front and back of the listener.
•
If you have a center rear cube speaker array
(Acoustimass 16 system or upgraded Acousti-
mass 15 Series II system), place it so that it is centered between the rear left and right cube
speaker arrays (see Figure 2).
Powered Acoustimass
®
module
Bose
®
Acoustimass speaker technology takes advantage of the fact that the source of pure
bass sound is difficult to locate, so you can hide the powered Acoustimass module conve-
niently out of sight. Place the module at the same end of the room as the television monitor.
• You may hide the module behind furniture, but do not block the opening. Be sure there is at
least 2 inches (5 cm) between any surface and the front opening or the grille on the bottom.
• If the opening faces the wall it increases the bass; if it faces away it decreases the bass.
CAUTION:
To prevent interference, keep the module at least 2 feet (.6m) from your TV set.
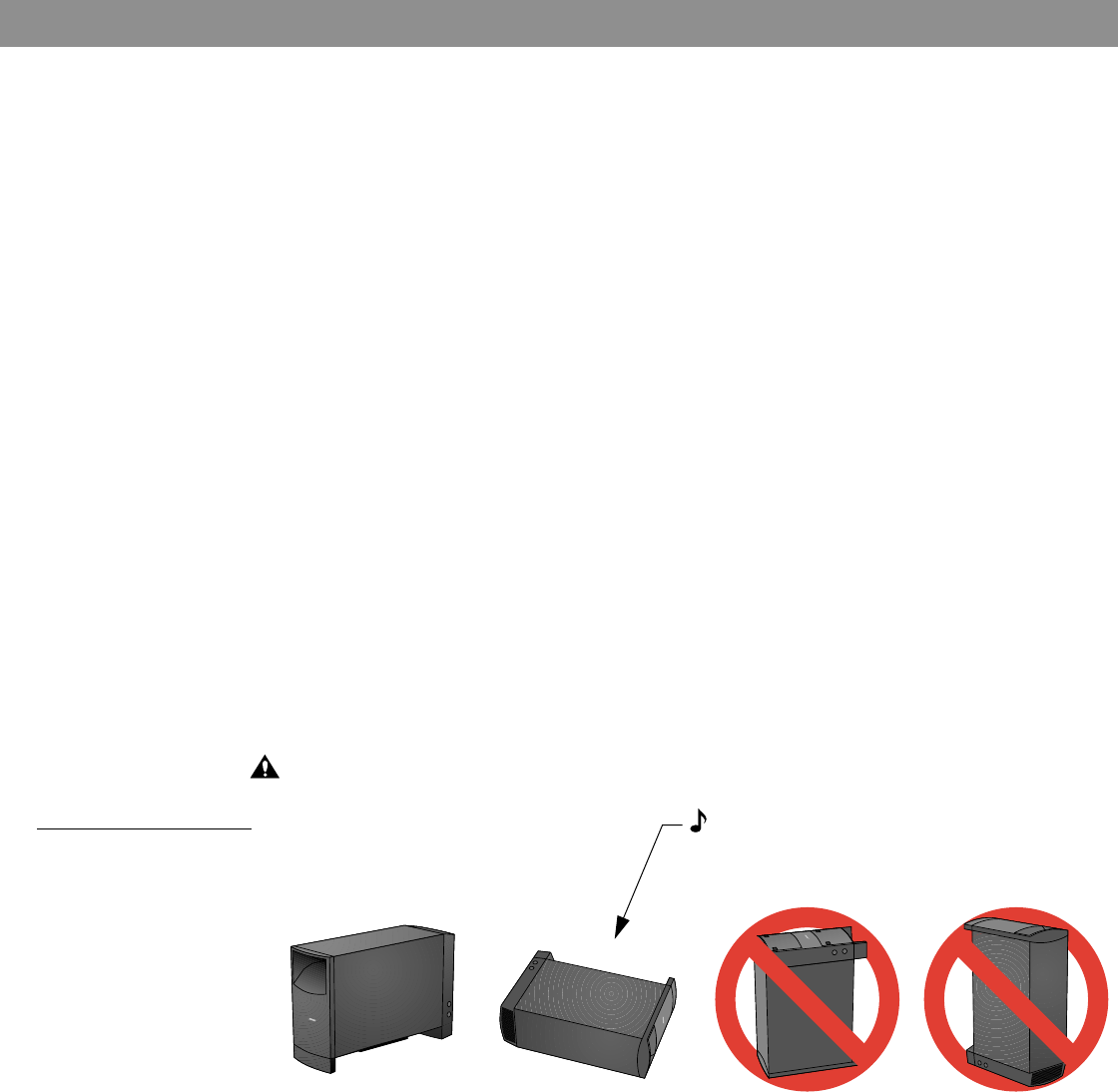
Figure 4
Powered Acoustimass
module placement
Note: Placing the module horizontally, or on
its side, may reduce ventilation, inhibiting its
ability to play at full output for extended
periods of time.
AM264924_00 _V.pdf • August 13, 2002