Connections
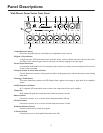
COM and GND Terminals
A shorting jumper typically connects the COM and GND terminals of the
amplifier together. The COM terminal is a common lead from the output
transformer. For the transformer-coupled speaker output to work, one of the
speaker load leads must be connected to this terminal.The GND terminal is
a connection to the system’s electrical ground and used when driving loads in
the Direct Out mode.
Connecting the GND to the COM terminal when using the transformer-cou-
pled outputs references the transformer output to ground. Disconnecting the
GND terminal from COM allows the transformer output to float electrically.
This is sometimes useful under certain conditions where a ground connection
is undesirable. It is generally a good idea, however, to short the GND to the
COM terminal regardless of output type (Trans or Direct).
Remote Volume Control
These terminals are provided for remote control of the Master Volume con-
trol.This control is motorized, allowing full control over the setting of the
master volume. The Bogen Remote Volume Control Panel (model RVCP)
provides a simple and elegant means of remote control. Shorting the UP ter-
minal with the C terminal will rotate the Master Volume control in a clock-
wise direction, increasing the volume level. Shorting the DN terminal to the
C terminal will cause the Master Volume control to rotate in a counter-
clockwise direction and decrease the level of the Master Volume control.The
impedance of the shorting connections must be less than 100 ohms in order
to operate the control.
Mute Control
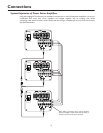
Each priority bus (High, Medium, and Low) can be externally activated.This
allows priority buses of two or more Wall-Mount Power Vector units to be
linked together for system expansion purposes. A particular mute
priority can be externally forced by shorting that priority’s bus terminal to
the C terminal of the Mute Control (the C terminal is the system ground).
Forcing the H priority bus this way will mute all modules except for modules
set for priority level 1 (highest priority). Forcing the M priority bus will mute
modules set for priority levels 3 or 4, but not levels 1 or 2, and forcing the
L priority bus will only mute modules set at priority level 4. See System
Expansion of Power Vector Amplifiers section and illustration on page 8.
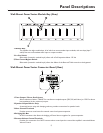
Bridging Mix Bus
This connector makes the Wall-Mount Power Vector’s mix bus available exter-
nally and allows the connecting of Power Vector units for system expansion
and simple room combining.
This function is bi-directional. Any signal received will be amplified and any
signal sent can be used by another Power Vector amp.The signal levels at the
bridging jack will drop by one-half with two Power Vectors tied together and
by two-thirds with three units tied together.Because of the attenuation of the
bridging signal, due to the signal loading of other Power Vectors, it is not
recommended that more than three units be connected together. See Mute
Control section and the illustration on the next page for additional information.
7